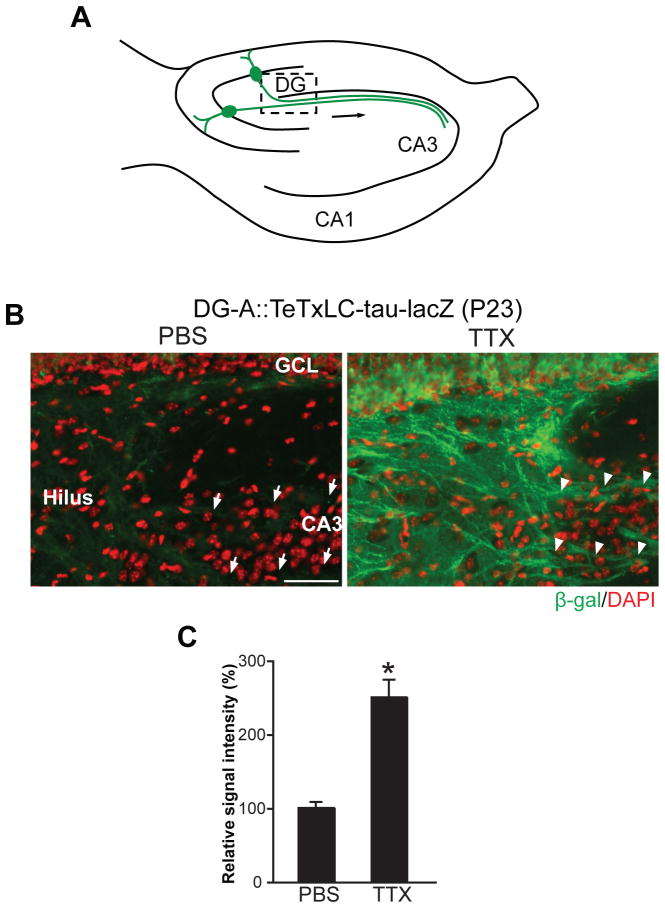
Figure 5. Global Suppression of Neural Activity Inhibits the Elimination of Inactive DG Axons in Mice in which Almost All DG Mature Neurons Are Inactivated.
(A) Schematic illustration of the hippocampus indicating the pictured area in (B).
(B) PBS- or TTX-containing Elvax was implanted on the hippocampus of DG-A::TeTxLC-tau-lacZ mice at P15 and their hippocampi were stained with the anti-β-gal antibody (green) at P23 to visualize TeTxLC-expressing axons (8 days total of TTX-Elvax application). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (red). In PBS-treated mice, few TeTxLC-expressing axons remained in CA3 (arrows). In contrast, in TTX-treated mice, many TeTxLC-expressing axons were maintained in CA3 (arrowheads). Scale bar is 50 μm.
(C) Quantification of the intensity of β-gal staining in the hilar region of PBS- or TTX-treated DG-A::TeTxLC-tau-lacZ mice. Data are shown as percentage of PBS control. Bars are mean ± SEM. Data are from 6 mice. Differs from the PBS-treated mice at *p < 0.01 by Student’s t-test.
See also Figure S3.