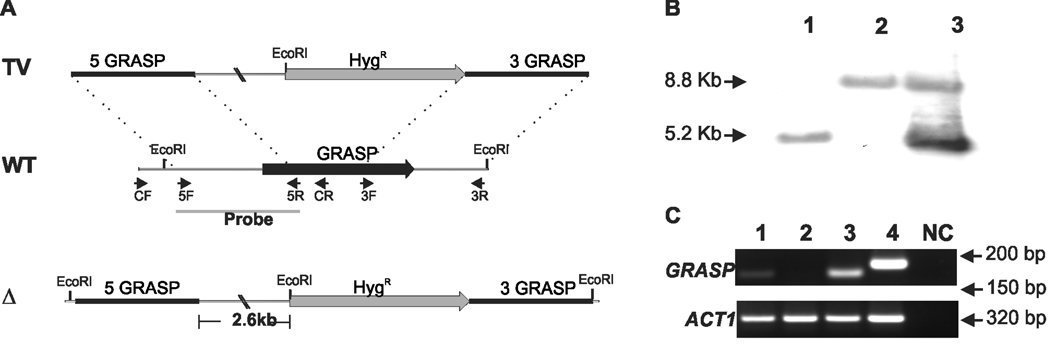
Figure 1. Deletion and complementation of the C. neoformans GRASP ortholog.
A. Scheme for the construction of the mutant strain. GRASP gene was replaced with the hygromicin resistant marker (HygR) cassette (gray box). GRASP 5’ and 3’ flanks (5 GRASP and 3 GRASP, respectively) were fused with HygR cassette by Delsgate methodology (Garcia-Pedrajas et al., 2008). The resulting targeting vector (TV) was used for C. neoformans transformation. The wild type locus of GRASP (WT) and the position of primers used for GRASP gene disruption are also indicated. The black bar scale corresponds to 500 base pairs (bp). The cleavage sites of EcoRI restriction enzyme are indicated in the deletion scheme. B. Southern blot analysis. Genomic DNA (10 µg) from WT (lane 1), grasp mutant (lane 2) and grasp::GRASP reconstituted (lane 3) strains were digested with EcoRI restriction enzyme. The 5’ gene flank was used as probe in Southern hybridization. Numbers at left indicate the hybridization signal sizes based upon the position of molecular size marker. C. Semi-quantitative RT-PCR with cDNA from WT (lane 1), grasp mutant (lane 2) and grasp::GRASP reconstituted (lane 3) strains as template. Numbers at rigth indicate the length of the transcript amplification for GRASP (upper panel) and ACT1 (lower panel) genes. Lane 4: positive control with genomic DNA as template. NC: negative control of the PCR reaction.