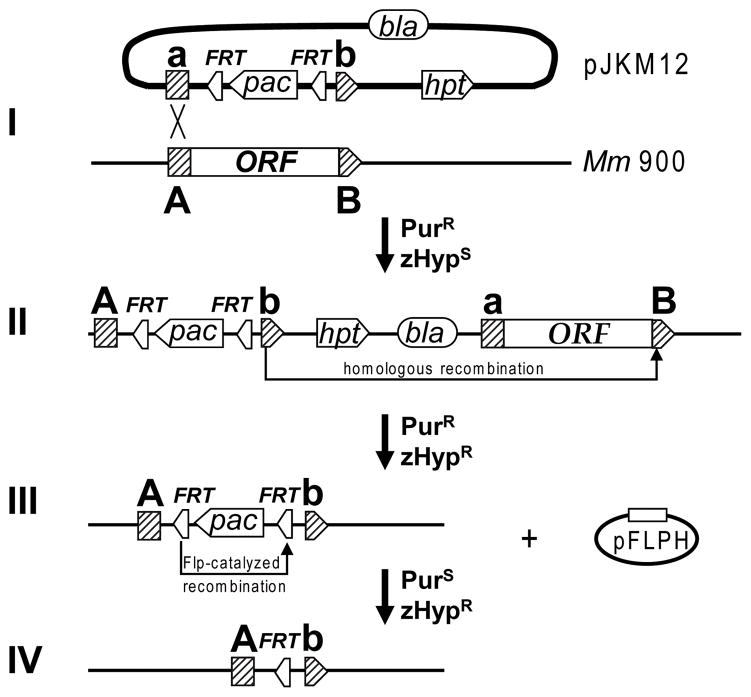
Fig. 2.
Generation of marked and markerless chromosomal deletions in M. maripaludis. (I) Plasmid pJKM12 which encodes M. maripaludis hpt, as well as a puromycin resistance cassette (pac) flanked by two flp recombinase recognition sites (FRT) and regions homologous to the target gene (a/A and b/B) is transformed into M. maripaludis Mm900 (Δhpt). (II) Integration of pJKM12 into the chromosome creates an unstable merodiploid state; a second homologous recombination event removes the vector backbone together with the wild-type allele of the target gene from the chromosome. (III) The target gene is replaced by pac bracketed by two FRT sites; cells are resistant to puromycin and zHyp. (IV) Expression of Flp recombinase from plasmid pFLPH results in removal of the puromycin cassette.