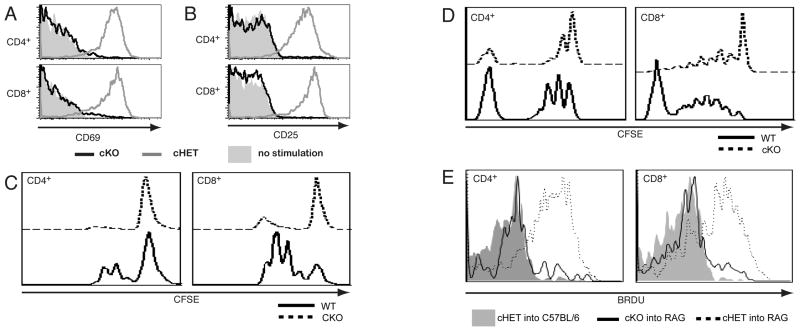
Figure 3. SLP-76 T is required in mature T cells for up-regulation of activation markers and for proliferation.
Splenocytes isolated from SLP-76cHET and SLP-76cKO mice were left unstimulated (shaded histograms) or were stimulated overnight with soluble anti-CD3 (open histograms). Cells were surface stained with CD4, CD8, CD69 and CD25. Expression of CD69 (A) and CD25 (B) on CD4+YFP+ and CD8+YFP+ are shown. Representative of greater than five experiments. (C) Splenocytes were labeled with CFSE and stimulated in vitro for seventy-two hours then stained with CD4 and CD8. Proliferation measured by dilution of CFSE in CD4 gated (left panel) and CD8 gated (right panel) are shown. SLP-76cKO cells are shown with a dotted line and SLP-76cHET by solid line. Representative of two experiments (D) CFSE-labeled Thy1.2+ T cells from SLP-76cHET and SLP-76cKO mice were adoptively transferred into RAG2−/−CD45SJL mice. Suspensions taken from lymph nodes seven days after transfer gated on CD45B6 donor, B220− then CD4 (left) or CD8 (right) are shown. Representative of two experiments. (E) Splenocytes from SLP-76cHet (dashed line) and SLP-76cKO (solid line) were adoptively transferred into CD45SJL and RAG2−/− CD45SJL recipients. BRDU was administered from during days 5 through 7. Lymph node suspensions gated on CD45B6 donor, YFP+ then CD4 (left) or CD8 (right) are shown. Shaded histograms represent BRDU incorporation into cells transferred into non-lymphopenic CD45SJL mice, where no LIP is expected. Representative of 2 experiments with a total of 9 recipient mice in each.