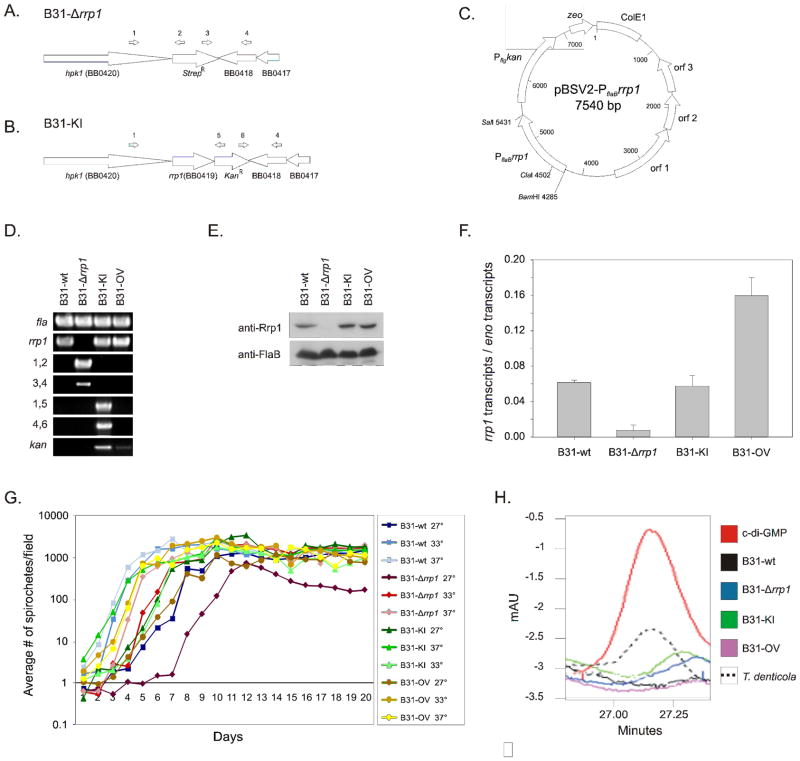
Figure 1. Generation and verification of rrp1 deletion, complementation, and overexpression strains and comparative analyses of their properties.
Schematics in panel A and B represent the chromosome of the B31-Δrrp1 and B31-KI complement mutants after allelic replacement, respectively. Schematic C depicts the pBSV2-PflaBrrp1 plasmid construct utilized in this study for the B31-OV mutant. Successful allelic exchange mutagenesis deleting and reinserting rrp1 was confirmed by PCR (Panel D), western blot (Panel E), and qRT-PCR analysis (Panel F). Verification of pBSV2-based overexpression of Rrp1 was likewise performed by PCR (Panel D), western blot (Panel E), and qRT-PCR (Panel F). Primers used for validation of proper integration are indicated by numbers above the schematic arrows and are listed to the left of the respective PCR panels. All primers used are listed in Table 1. The error bars in panel F indicate the standard deviation. Growth of each strain was assessed at 27, 33 and 37° over 20 days in BSK-H complete media. In panel H, HPLC chromatograms of nucleotide extracts from each strain are presented. The elution time of purified c-di-GMP is shown for reference. T. denticola nucleotide extracts were assessed as a positive control. All methods were as described in the text.