Abstract
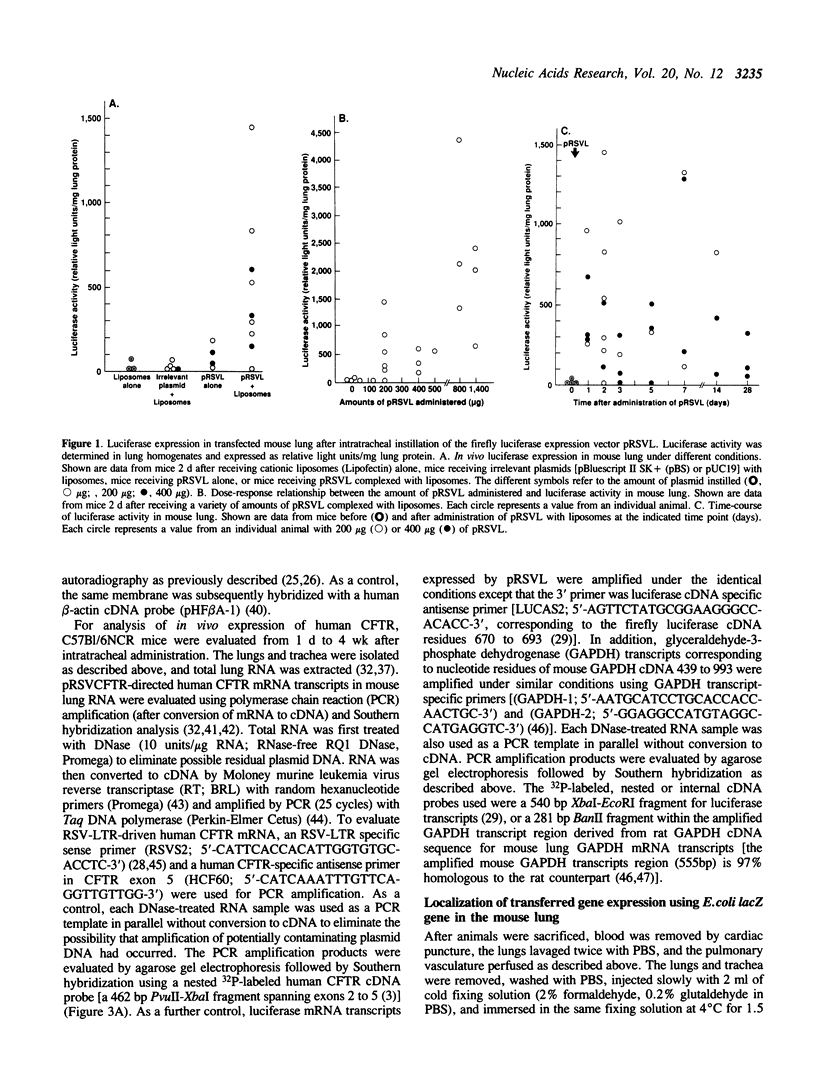
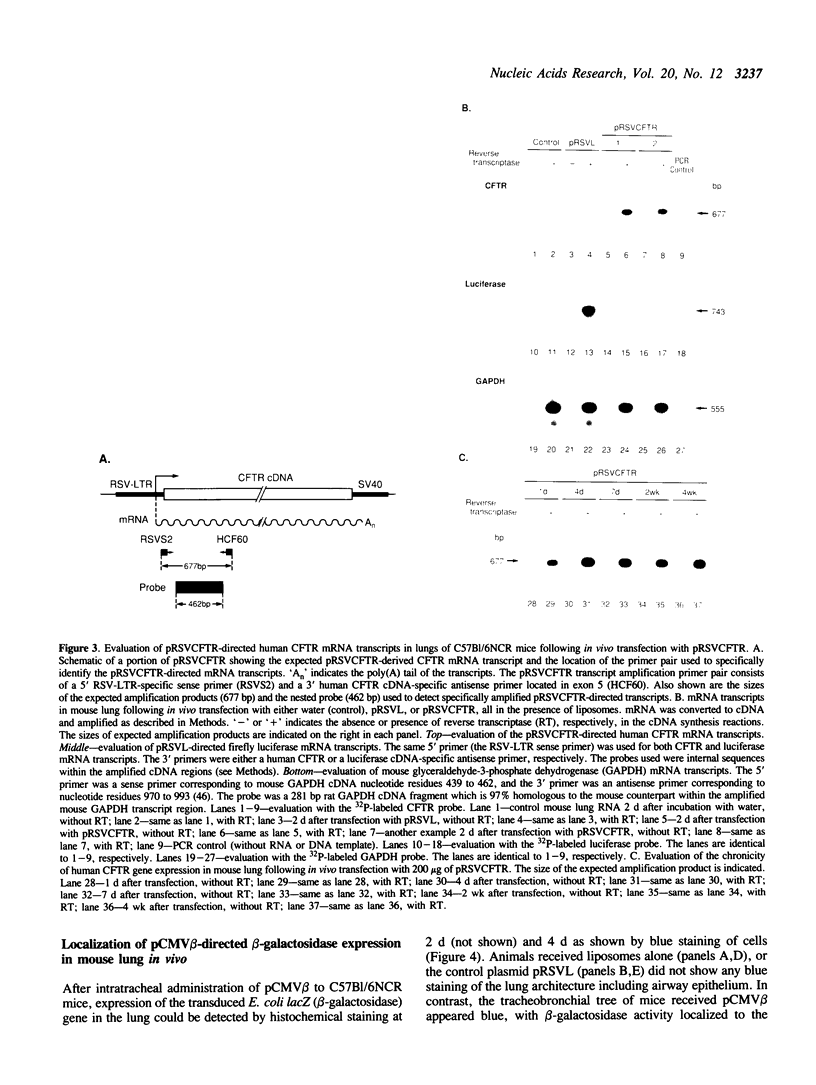
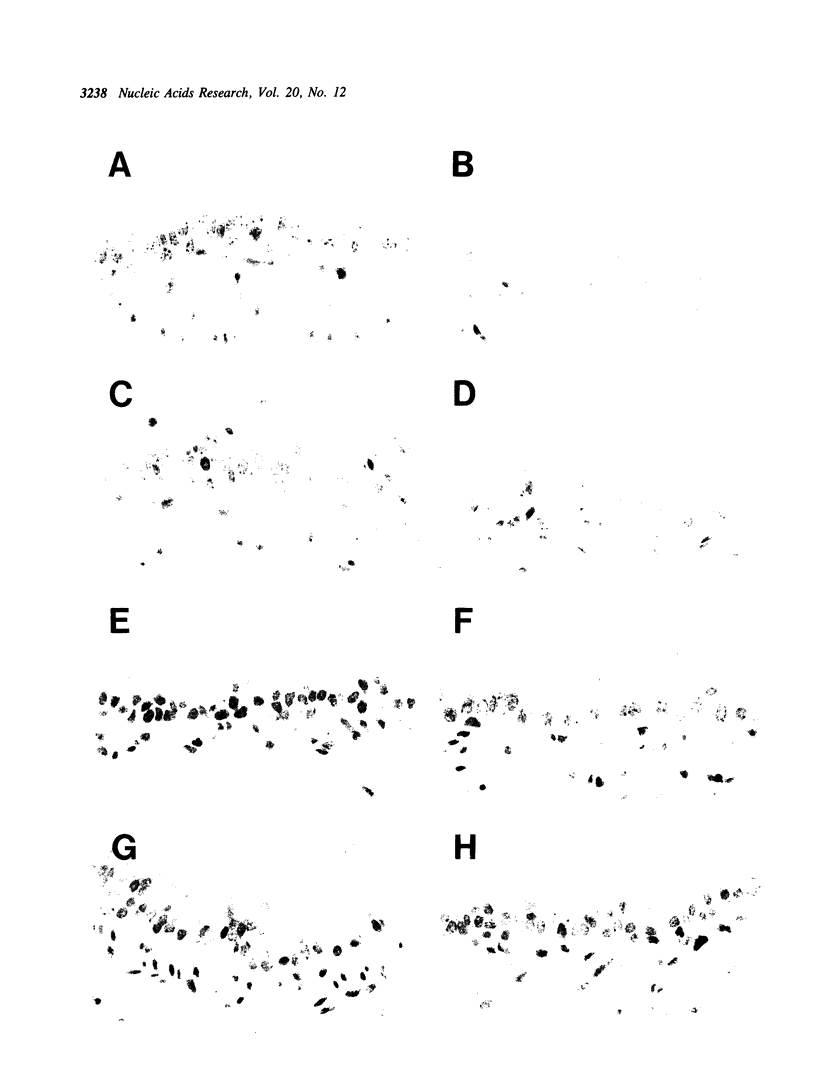
As an approach to gene therapy for the respiratory manifestations of cystic fibrosis (CF), in vivo plasmid-mediated direct transfer of the normal CF transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene to the airway epithelium was investigated in mice. To evaluate the feasibility of this strategy, pRSVL, a plasmid composed of a firefly luciferase gene driven by the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat (RSV-LTR), along with cationic liposomes was instilled into the trachea of C57BI/6NCR mice. With administration of 200-400 micrograms plasmid DNA, luciferase expression could be detected in the mouse lung homogenates for at least 4 wk. With this background, a CFTR expression plasmid vector (pRSVCFTR) constructed by replacing the luciferase cDNA from pRSVL with the normal human CFTR cDNA was evaluated in vivo in mice. Intratracheal instillation of pRSVCFTR with cationic liposomes followed by analysis of mouse lung RNA by polymerase chain reaction amplification (after conversion of mRNA to cDNA) using a RSV-LTR specific sense primer and a human CFTR-specific antisense primer demonstrated human CFTR mRNA transcripts from one day to 4 wk after instillation. Further, in vivo evaluation of beta-galactosidase activity after intratracheal administration of an E. coli lacZ gene expression plasmid vector directed by the cytomegalovirus promoter (pCMV beta) demonstrated that the airway epithelium was the major target of transfer and expression of the exogenous gene. These observations demonstrate successful plasmid-mediated gene transfer to the airway epithelium in vivo. This strategy may be feasible as a form of gene therapy to prevent the pulmonary manifestations of CF.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. P., Gregory R. J., Thompson S., Souza D. W., Paul S., Mulligan R. C., Smith A. E., Welsh M. J. Demonstration that CFTR is a chloride channel by alteration of its anion selectivity. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):202–205. doi: 10.1126/science.1712984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. P., Rich D. P., Gregory R. J., Smith A. E., Welsh M. J. Generation of cAMP-activated chloride currents by expression of CFTR. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):679–682. doi: 10.1126/science.1704151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear C. E., Duguay F., Naismith A. L., Kartner N., Hanrahan J. W., Riordan J. R. Cl- channel activity in Xenopus oocytes expressing the cystic fibrosis gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19142–19145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger H. A., Anderson M. P., Gregory R. J., Thompson S., Howard P. W., Maurer R. A., Mulligan R., Smith A. E., Welsh M. J. Identification and regulation of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-generated chloride channel. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1422–1431. doi: 10.1172/JCI115450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. H., Rich D. P., Marshall J., Gregory R. J., Welsh M. J., Smith A. E. Phosphorylation of the R domain by cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulates the CFTR chloride channel. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):1027–1036. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90446-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting G. R., Kasch L. M., Rosenstein B. J., Tsui L. C., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Antonarakis S. E. Two patients with cystic fibrosis, nonsense mutations in each cystic fibrosis gene, and mild pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 13;323(24):1685–1689. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012133232407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting G. R., Kasch L. M., Rosenstein B. J., Zielenski J., Tsui L. C., Antonarakis S. E., Kazazian H. H., Jr A cluster of cystic fibrosis mutations in the first nucleotide-binding fold of the cystic fibrosis conductance regulator protein. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):366–369. doi: 10.1038/346366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. Cystic fibrosis. Complementary endeavours. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):110–111. doi: 10.1038/348110a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., White M. B., Amos J., Gerrard B., Stewart C., Khaw K. T., Leppert M. Multiple mutations in highly conserved residues are found in mildly affected cystic fibrosis patients. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):863–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90196-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drumm M. L., Pope H. A., Cliff W. H., Rommens J. M., Marvin S. A., Tsui L. C., Collins F. S., Frizzell R. A., Wilson J. M. Correction of the cystic fibrosis defect in vitro by retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1227–1233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Rechkemmer G., Shoemaker R. L. Altered regulation of airway epithelial cell chloride channels in cystic fibrosis. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):558–560. doi: 10.1126/science.2425436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory R. J., Cheng S. H., Rich D. P., Marshall J., Paul S., Hehir K., Ostedgaard L., Klinger K. W., Welsh M. J., Smith A. E. Expression and characterization of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. Nature. 1990 Sep 27;347(6291):382–386. doi: 10.1038/347382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang T. C., Lu L., Zeitlin P. L., Gruenert D. C., Huganir R., Guggino W. B. Cl- channels in CF: lack of activation by protein kinase C and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1351–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.2472005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartner N., Hanrahan J. W., Jensen T. J., Naismith A. L., Sun S. Z., Ackerley C. A., Reyes E. F., Tsui L. C., Rommens J. M., Bear C. E. Expression of the cystic fibrosis gene in non-epithelial invertebrate cells produces a regulated anion conductance. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):681–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90498-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerem B., Rommens J. M., Buchanan J. A., Markiewicz D., Cox T. K., Chakravarti A., Buchwald M., Tsui L. C. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1073–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.2570460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lethem M. I., James S. L., Marriott C., Burke J. F. The origin of DNA associated with mucus glycoproteins in cystic fibrosis sputum. Eur Respir J. 1990 Jan;3(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., McCann J. D., Liedtke C. M., Nairn A. C., Greengard P., Welsh M. J. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase opens chloride channels in normal but not cystic fibrosis airway epithelium. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):358–360. doi: 10.1038/331358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor G. R., Caskey C. T. Construction of plasmids that express E. coli beta-galactosidase in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2365–2365. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. G., Adam M. A., Miller A. D. Gene transfer by retrovirus vectors occurs only in cells that are actively replicating at the time of infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4239–4242. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picot R., Das I., Reid L. Pus, deoxyribonucleic acid, and sputum viscosity. Thorax. 1978 Apr;33(2):235–242. doi: 10.1136/thx.33.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich D. P., Anderson M. P., Gregory R. J., Cheng S. H., Paul S., Jefferson D. M., McCann J. D., Klinger K. W., Smith A. E., Welsh M. J. Expression of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator corrects defective chloride channel regulation in cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. Nature. 1990 Sep 27;347(6291):358–363. doi: 10.1038/347358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich D. P., Gregory R. J., Anderson M. P., Manavalan P., Smith A. E., Welsh M. J. Effect of deleting the R domain on CFTR-generated chloride channels. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):205–207. doi: 10.1126/science.1712985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommens J. M., Dho S., Bear C. E., Kartner N., Kennedy D., Riordan J. R., Tsui L. C., Foskett J. K. cAMP-inducible chloride conductance in mouse fibroblast lines stably expressing the human cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7500–7504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommens J. M., Iannuzzi M. C., Kerem B., Drumm M. L., Melmer G., Dean M., Rozmahel R., Cole J. L., Kennedy D., Hidaka N. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: chromosome walking and jumping. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1059–1065. doi: 10.1126/science.2772657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. A., Siegfried W., Yoshimura K., Yoneyama K., Fukayama M., Stier L. E., Päkkö P. K., Gilardi P., Stratford-Perricaudet L. D., Perricaudet M. Adenovirus-mediated transfer of a recombinant alpha 1-antitrypsin gene to the lung epithelium in vivo. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):431–434. doi: 10.1126/science.2017680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. J., Tanese N., Goff S. P. Purification and characterization of murine retroviral reverse transcriptase expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9326–9335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupprecht A. P., Coleman D. L. Transfection of adherent murine peritoneal macrophages with a reporter gene using DEAE-dextran. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Nov 22;144(2):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90082-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath D. E., Broome H. E., Prystowsky M. B. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA is a major interleukin 2-induced transcript in a cloned T-helper lymphocyte. Gene. 1990 Jul 16;91(2):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Rubenstein J. L., Nicolas J. F. Use of a recombinant retrovirus to study post-implantation cell lineage in mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapnell B. C., Chu C. S., Paakko P. K., Banks T. C., Yoshimura K., Ferrans V. J., Chernick M. S., Crystal R. G. Expression of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene in the respiratory tract of normal individuals and individuals with cystic fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6565–6569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapnell B. C., Zeitlin P. L., Chu C. S., Yoshimura K., Nakamura H., Guggino W. B., Bargon J., Banks T. C., Dalemans W., Pavirani A. Down-regulation of cystic fibrosis gene mRNA transcript levels and induction of the cystic fibrosis chloride secretory phenotype in epithelial cells by phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10319–10323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Sun X. H., Kao T. H., Reece K. S., Wu R. Isolation and characterization of rat and human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNAs: genomic complexity and molecular evolution of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2485–2502. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. B., Amos J., Hsu J. M., Gerrard B., Finn P., Dean M. A frame-shift mutation in the cystic fibrosis gene. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):665–667. doi: 10.1038/344665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Identification of a functional promoter in the long terminal repeat of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90555-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura K., Nakamura H., Trapnell B. C., Chu C. S., Dalemans W., Pavirani A., Lecocq J. P., Crystal R. G. Expression of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene in cells of non-epithelial origin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 11;19(19):5417–5423. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.19.5417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura K., Nakamura H., Trapnell B. C., Dalemans W., Pavirani A., Lecocq J. P., Crystal R. G. The cystic fibrosis gene has a "housekeeping"-type promoter and is expressed at low levels in cells of epithelial origin. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9140–9144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]