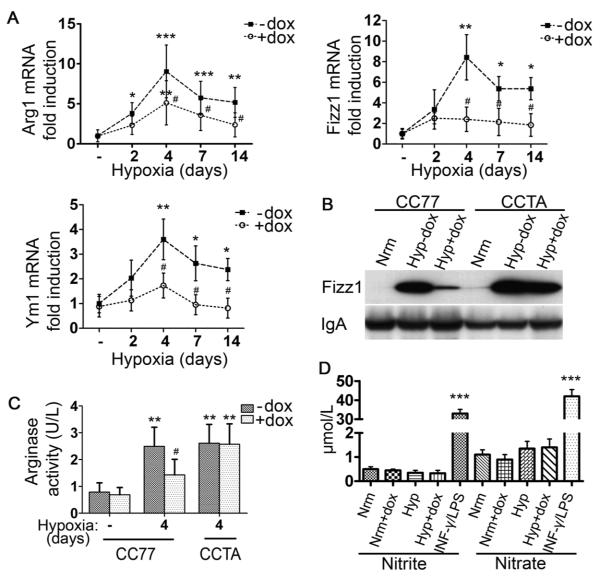
Figure 4. Hypoxia induces alternatively-activated macrophages: the suppressive effect of HO-1.
[A] qPCR analysis of hypoxic alveolar macrophage mRNA isolated from bitransgenic mice (CC77) revealed increased Arg1, Fizz1, and Ym1 levels that were suppressed with dox. [B] Western blot analysis for Fizz1 on BALF from normoxic mice (Nrm) and mice exposed to hypoxia for 4 days -dox (Hyp−dox) or with dox treatment (Hyp+dox). IgA served as internal control. [C] Arginase activity (U/L) was assessed by urea formation in alveolar macrophages from normoxic and hypoxic animals. [D] iNOS activity was estimated by the levels of nitrite and nitrate in the BALF of hypoxic mice. Supernatants from RAW 264.7 macrophages stimulated with 100 μg/ml LPS E.coli and 100 U/ml INF-γ for 48 hours served as positive controls. Mean ± SD is depicted for n≥6 mice per group. *: relative to normoxia; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. #:relative to hypoxia –dox; #p<0.05, ##p<0.01, ###p<0.001.