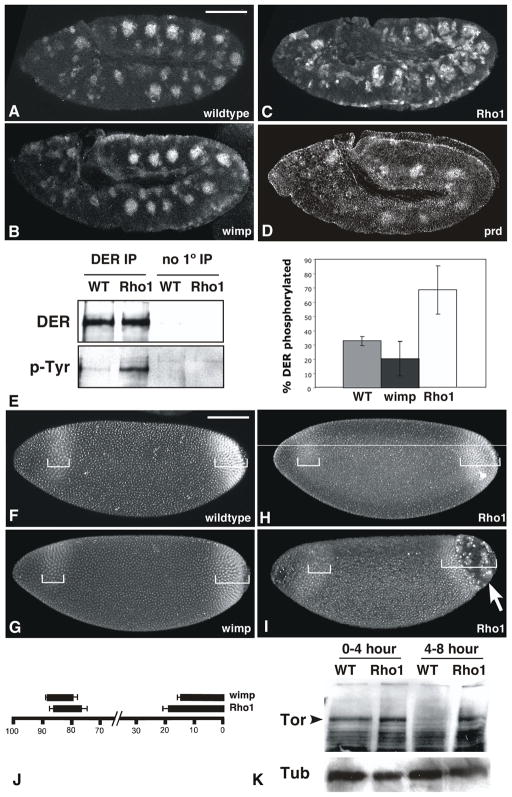
Figure 5. Maternal Rho1 mutants are generally defective in endocytosis.
(A–D) Wildtype (A), wimp/+ (B) maternal Rho1 mutant (C), and prd (D) mutant embryos labeled with antibodies to dpERK and visualized with immunofluorescence. Note the ectopic accumulation of dpERK in Rho1 mutants relative to wildtype, wimp/+, and prd controls. (E) Drosophila EGFR (DER) was immunoprecipitated from wildtype, wimp/+ and maternal Rho1 mutant embryo lysates. Western analysis was used to identify the overall amount of DER protein immunoprecipitated and its phosphorylation state. The graph indicates the amount of phosphotyrosine detected relative to the total amount of DER protein. (F–I) Wildtype (F), wimp/+ (G), and maternal Rho1 mutant (H, I) embryos labeled with antibodies against Tll. Brackets indicate the extent of the anterior and posterior expression domains. Note the posterior cellularization defect indicated by the arrow in I. (J) Quantitation of the extent of Tll expression domains, expressed as % embryo length. (K) Western analysis of Torso protein levels in 0–4 and 4–8 hour wildtype and maternal Rho1 embryo lysates. 50μg of total protein loaded per lane, Tubulin levels shown as loading control. Scale bars: 100μm.