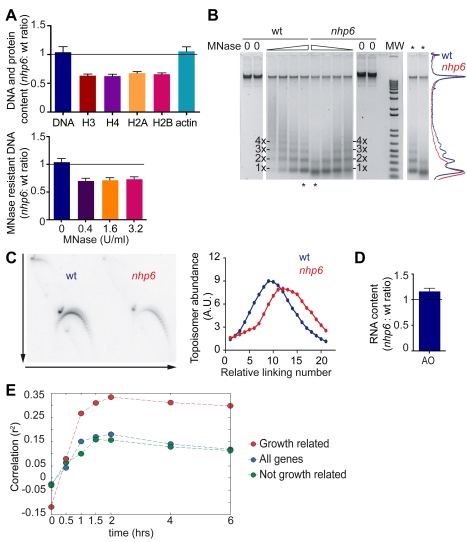
Figure 5. nhp6 cells contain fewer nucleosomes and more RNA transcripts.
(A) Quantification of histone content (upper panel) from western blots of wild type and nhp6 cells; the decreases in core histone contents are statistically significant (p<0.05, Wilcoxon test). Lower panel: residual (nucleosome-protected) DNA obtained from nhp6 and wild type cells after digestion with increasing MNase concentrations. Error bars represent SEM from three biological replicates. (B) Electrophoretic separation of DNA samples from 3×108 wild type and nhp6 cells after MNase digestion (from 6.4 U/ml in 2× dilutions). The densitometric analysis of the central two lanes (asterisks) is shown on the right. (C) Topological analysis of yRp17 plasmid in wild type and nhp6 cells by 2D-electrophoresis in the presence of different amounts of chloroquine in orthogonal directions (arrows in the left panel). Quantification of the different DNA topoisomers is shown in the right panel. (D) RNA quantification in wild type and nhp6 cells by Acridine Orange staining. Error bars, SEM of three biological replicates. RNA ratio is significantly different from 1 (p<0.05 Wilcoxon test). (E) Correlation over time between gene expression profiles of UKY403 and nhp6 cells. Time 0 corresponds to the galactose to glucose shift for the UKY403 strain.