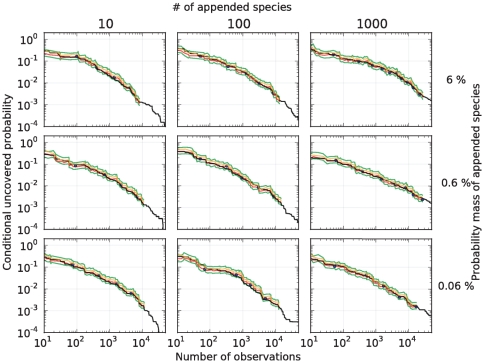
Figure 7. Predictions in the human-gut urn when simulating the rare biosphere.
In a sample of size 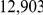 from a human-gut,
from a human-gut, 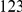 species were discovered. Based on our methods, we estimate that
species were discovered. Based on our methods, we estimate that 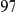 of these species represent
of these species represent 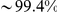 of that gut environment; hence, the remaining
of that gut environment; hence, the remaining 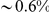 is composed by at least
is composed by at least 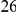 species. To test our predictions of the conditional uncovered probability (black), we simulated the rare biosphere by adding additional species and hypothesized that our point prediction could be offset by up to one order of magnitude: point predictions produced by the Embedding Algorithm (blue), point predictions produced by the algorithm each time a new species was discovered (red),
species. To test our predictions of the conditional uncovered probability (black), we simulated the rare biosphere by adding additional species and hypothesized that our point prediction could be offset by up to one order of magnitude: point predictions produced by the Embedding Algorithm (blue), point predictions produced by the algorithm each time a new species was discovered (red), 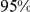 upper-bound (orange), and
upper-bound (orange), and 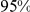 conservative-upper interval (green). The predictions used the parameters
conservative-upper interval (green). The predictions used the parameters 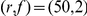 . The different urns were devised as follows. For each
. The different urns were devised as follows. For each 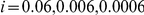 (indexing rows) and
(indexing rows) and 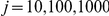 (indexing columns), a mixture of two urns was considered: an urn with the same distribution as the microbes found in the gut dataset, and weighted by the factor
(indexing columns), a mixture of two urns was considered: an urn with the same distribution as the microbes found in the gut dataset, and weighted by the factor  , and an urn consisting of
, and an urn consisting of 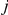 colors (disjoint from the gut urn), with an exponentially decaying rank curve and weighted by the factor
colors (disjoint from the gut urn), with an exponentially decaying rank curve and weighted by the factor  . See Fig. 5 for the rank curve associated with each urn.
. See Fig. 5 for the rank curve associated with each urn.