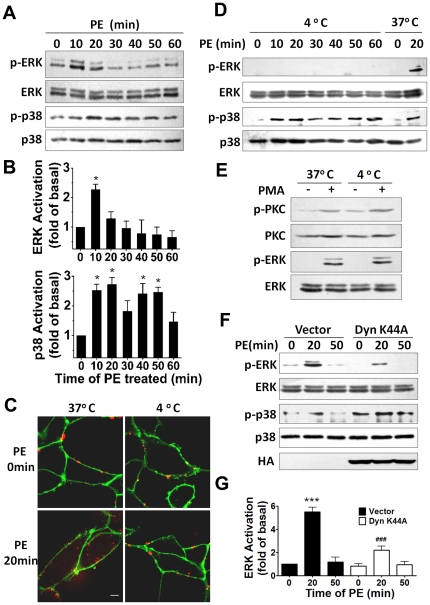
Figure 3. Receptor endocytosis is involved in ERK1/2 activation by α1A-AR stimulation.
(A) Representative western blot showing activation of ERK1/2 and p38 after 10-µM PE treatment for the indicated times. (B) Relative ERK1/2 and p38 activeity after PE stimulation are shown. Data are means±SEM of results obtained in three independent experiments. Statistical significance of the difference was assessed using one-way ANOVA analysis. *, p<0.05 versus 0 min. (C) Effect of 4°C chilling on agonist-induced α1A-AR endocytosis. Cells were incubated in 4°C or 37°C for 30 min then stimulated with 10 µM PE for 20 min. α1A-ARs were detected with anti-FLAG antibody and Alexa-555 IgG (red), and plasma membrane was labeled with Alexa 488-conjugated WGA (green). (D) Western blot analysis of ERK1/2 and p38 phosphorylation with PE stimulation for the indicated times at 4°C. Stimulation at 37°C is a control. (E) Phorbol 12-myristate, 13-acetate (PMA)-induced activation of protein kinase C (PKC) and ERK1/2 at 4°C. Cells were incubated in 4°C or 37°C for 30 min then stimulated with 0.1 µM PMA for 20 min. (F) Dynamin mutation inhibits the activation of ERK1/2 by α1A-AR. HEK-293A–α1A-AR cells were cultured and infected with Dyn-K44A or vectors. After 40 h, cells were treated for 20 min with 10 µM PE. Protein expression of phospho-ERK1/2 and total ERK1/2 and p38 were measured. Expression of Dyn-K44A (HA-tagged) was identified with blotting of HA-tag. (G) Quantification of relative ERK1/2 activation corresponding to (F) was performed by densitometric analysis. Data are means±SEM of results obtained in three independent experiments. Statistical significance of the difference was assessed using one-way ANOVA analysis. ***, p<0.001 versus Vector 0 min. ###, p<0.001 versus Vector 20 min.