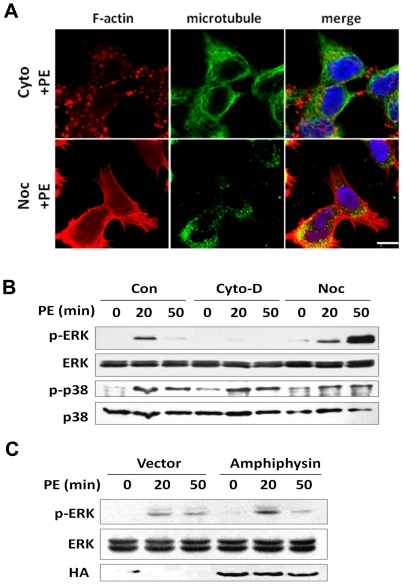
Figure 4. Actin organization is involved in ERK1/2 activation induced by α1A-AR.
(A) Effect of actin and microtubule-disrupting drugs on cytoskeleton organization after agonist stimulation. HEK-293A–α1A-AR cells were pre-incubated with cytochalasin-D (Cyto-D; 5 µM, 5 min) or nocodazole (noc; 20 µM, 20 min) at 37°C, then stimulated with 10 µM PE for 20 min. F-actin was stained by TRITC-conjugated Phalloidin (red), and microtubules were stained with anti-α-tubulin antibody and Alexa-488 IgG (green). Nuclei were stained with Hochest-33342 (blue). Bar: 10 µm. (B) Effect of cytoskeleton disrupton on the activation of ERK1/2 and p38 after α1A-AR stimulation. HEK-293A–α1A-AR cells were pre-incubated with Cyto-D (5 µM, 5 min) or nocodazole (20 µM, 20 min) in 37°C, then treated with 10 µM PE for 20 and 50 min. Cell lysates were immunoblotted for the phosphrylation of ERK1/2 and p38. (C) Overexpression of amphiphysin enhanced the activation of ERK1/2 after agonist stimulation. HEK-293A–α1A-AR cells were transfected with amphiphysin plasmid, then treated with 10 µM PE for 20 and 50 min. Cell lysates were immunoblotted for analysis of phospho and total ERK1/2.