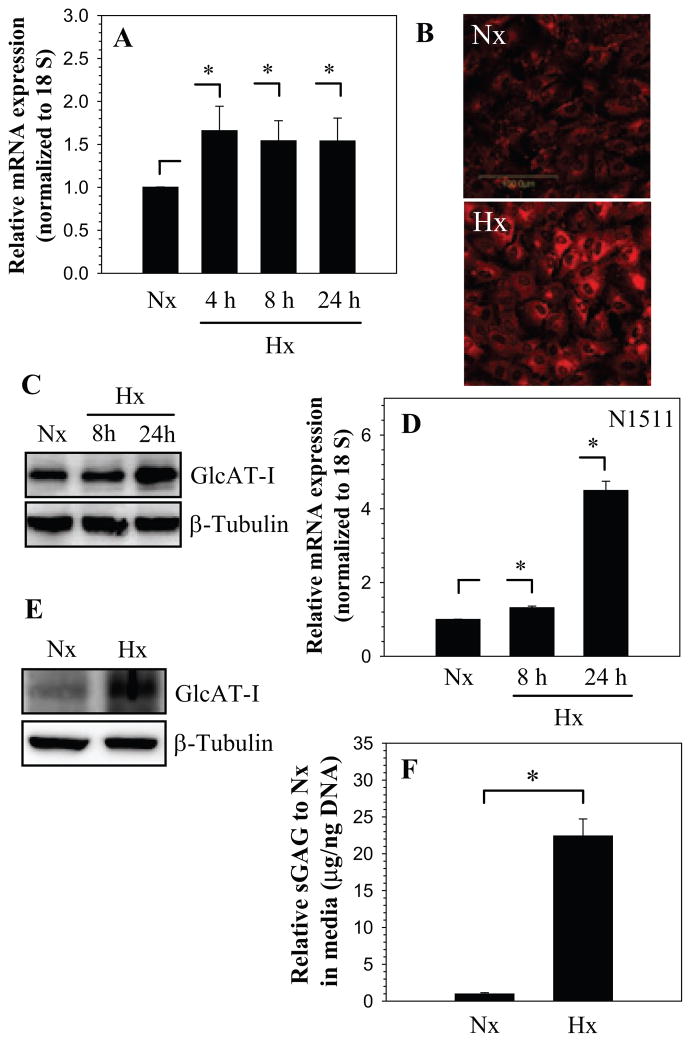
Figure 1.
A) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of GlcAT-I expression by nucleus pulposus cells cultured in hypoxia (1% O2) up to 24 h. There was increased expression at 4 h which continued till 24 h. B) Immunofluorescent analysis of nucleus pulposus cells in hypoxia. Cells showed increased GlcAT-I expression 24 h after the treatment. C) Western blot analysis of GlcAT-I expression by nucleus pulposus cells. Note, the expression of the 43 kd GlcAT-I band. Note, increased GlcAT-I levels after 24 h in hypoxia. D) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of GlcAT-I expression by N1511 chondrocytes cultured in hypoxia (1% O2) for 24 h. Hypoxia increased expression of GlcAT-I in chondrocytes. E) Western blot analysis showing increased expression of GlcAT-I by N1511 cells in hypoxia. F) Hypoxia significantly increased sGAG production by nucleus pulposus cells. Values shown are mean ± SE, of 3 independent experiments; *p<0.05.