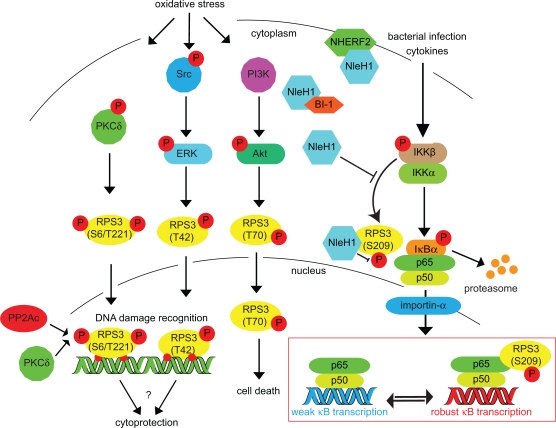
Figure 2.
Inducing RPS3 phosphorylation via oxidative stress, DNA damage, and bacterial infection. RPS3 phosphorylation is activated by a variety of cellular stressors. The specific phosphorylation sites and the protein kinases responsible (PKCδ, ERK, Akt) are indicated. Nuclear RPS3 is also bound by the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2Ac). IKKβ phosphorylates RPS3 S209 in response to cytokines or bacterial infection. This phosphorylation can be inhibited by the E. coli NleH1 protein, which also binds the BI-1 and NHERF2 proteins.