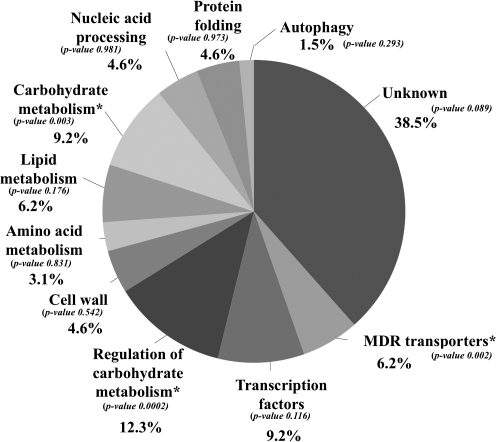
FIG. 4.
Clustering, based on biological function, of genes activated in response to acetic acid stress in a Haa1p-dependent way. Genes whose transcript level in yeast cells challenged with acetic acid was reduced by more than 25% in the Δhaa1 mutant, compared to the levels attained in the parental strain, were grouped according to their biological functions described on MIPS functional catalog. The relative percentage of each functional class was calculated taking into consideration the number of genes in each class compared to the total of Haa1p-regulated genes (85) considered and the p-values of each functional class. Enriched classes (p-value below 0.01) are marked with*.