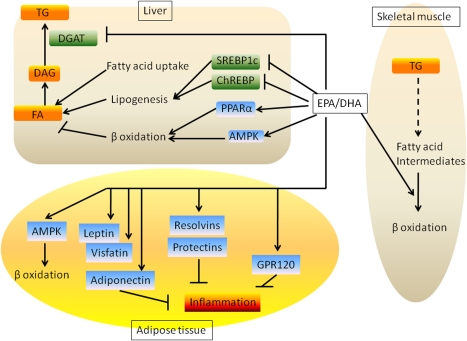
Figure 3.
Integrated effects of EPA and DHA on liver, skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue metabolism. EPA and DHA promote hepatic fatty acid oxidation and suppress lipogenesis. This leads to reduced accumulation of TG in the liver. These fatty acids also increase adipose tissue fatty acid oxidation and increase secretion of adiponectin, leptin, and visfatin. EPA and DHA also alleviate adipose tissue inflammation via GPR120 and resolvins/protectins. In the skeletal muscle, EPA and DHA promote fatty acid oxidation, thereby preventing accumulation of fatty acid intermediates. All these mechanisms account for the EPA- and DHA-mediated improvement in insulin sensitivity.