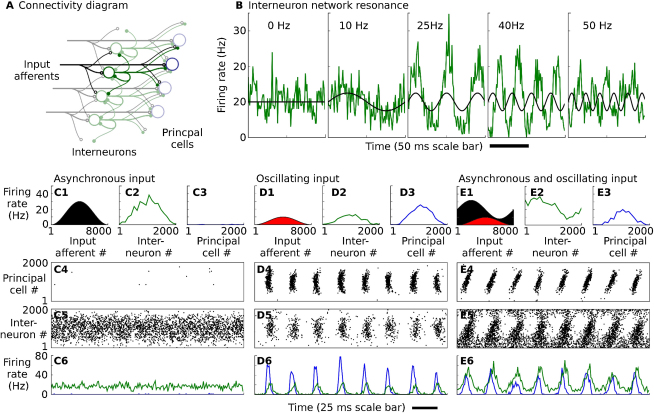
Figure 4.
Filter Network
(A) Diagram of filter network connectivity showing the input afferents (black), feed-forward interneuron layer (green), and principal cells (blue).
(B) Resonance in filter network interneuron population activity. Panels show the firing rate of the interneuron population (green) driven by periodically modulated Poisson spike input (mean rate indicated in black) at a range of frequencies bracketing the network resonance frequency (see Figure S1 as well).
(C–E) Filter network principal cells reproduce position of oscillating input activity, irrespective of spatial pattern of asynchronous input. Filter network activity is driven by (C) asynchronous input, (D) gamma-modulated input, (E) mixed gamma-modulated and asynchronous input. (C1, D1, E1) Spatial pattern of firing rates in afferent fibers (black: asynchronous Poisson input, Poisson input sinusoidally modulated at 40 Hz). (C2, D2, E2) Spatial pattern of the firing rate in the interneuron layer. (C3, D3, E3) Spatial pattern of the firing rate in the principal cell layer. (C4, D4, E4) Spike raster for principal cells. (C5, D5, E5) Spike raster for interneurons. (C6, D6, E6) Firing rate of principal cell (blue) and interneuron (green) populations. See Figure S2 as well.