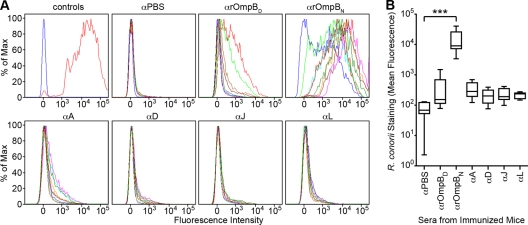
Fig. 3.
Surface recognition of R. conorii by IgG in a subset of rOmpB-immunized animals. (A) Flow cytometric analyses of R. conorii recognition by immunized mouse sera. Sera from PBS- and rOmpB-immunized C3H/HeN mice were analyzed by flow cytometry for IgG antibodies that could recognize rOmpB epitopes on the R. conorii surface. Sera collected from actively immunized mice were diluted 1/1,000 and used to stain PFA-fixed R. conorii. Mouse antibody recognition of R. conorii was detected using a secondary goat anti-mouse IgG Alexa Fluor 546 conjugate. Controls (top left) show the fluorescence intensity shift between naïve mouse serum-labeled (blue) and anti-R. conorii mouse serum-labeled (red) R. conorii. Sera from eight PBS- or nine rOmpB-immunized mice per group were analyzed. The fluorescence spectrum of each mouse is displayed in a different color. At least 8,000 R. conorii organisms were measured per spectrum. (B) Box-and-whisker plots of the combined mean fluorescence from the flow cytometric analyses of the serum staining of R. conorii done in panel A. The box encompasses the 25 to 75% quartile, with the inner line representing the median and the whiskers denoting the minimum and maximum mean fluorescence values for each of the sera from the seven groups of immunized mice. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett's test was used for group comparisons. ***, P < 0.001.