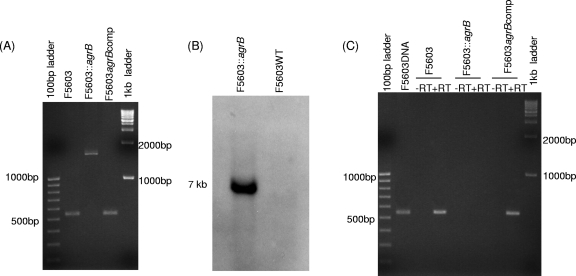
Fig. 1.
Intron-based mutagenesis to create an isogenic F5603 agrB mutant and construction of a complementing strain. (A) PCR confirmation of the isogenic agrB null mutant and complementing strain. Using internal agrB primers, this PCR assay amplifies an ∼500-bp product from the wild-type agrB gene, but due to the presence of a 900-bp intron insertion, it amplifies an ∼1.5-kb PCR product from an intron-disrupted agrB gene. (B) Southern blot hybridization of an intron-specific probe to DNA from wild-type F5603 or the agrB null mutant. DNA from each strain was digested with EcoRI prior to electrophoresis on a 1% agarose gel prior to blotting and hybridization with an intron-specific probe. Size of DNA fragments, in kilobases (kb), is shown at the left. (C) RT-PCR analyses for agrB expression by F5603, the F5603::agrB mutant, and the complementing F5603agrBcomp strain grown for 5 h in DS medium. First and last lanes show size markers. Lanes labeled with a plus sign (+) were from samples receiving reverse transcriptase, while lanes labeled with a minus sign (−) lacked reverse transcriptase to show the absence of DNA contamination.