Figure 4.
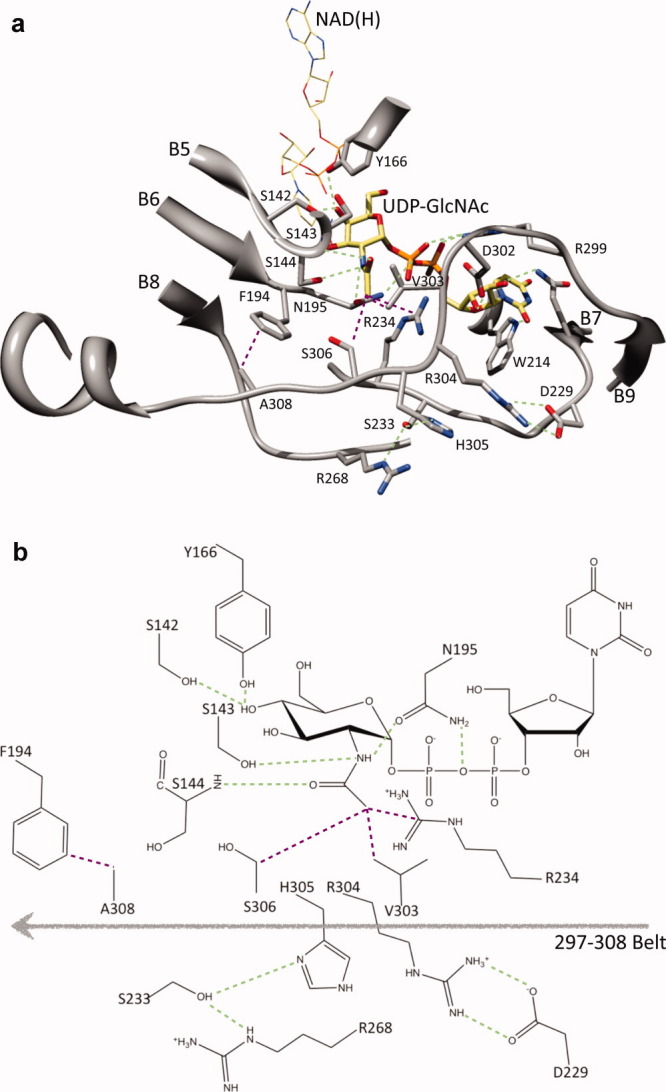
Architecture of the substrate binding region of WbgU. A salt bridge between Arg304 and Asp229 on one side and a hydrogen bonding network formed between His305, Ser233, and Arg268 launch the substrate binding region in a conformation that results in the formation of a hydrophobic cluster contributed by Val303, Arg234, and Ser303. This hydrophobic cluster directly interact with the CH3- group of the GlcNAc moiety. In addition, this conformation results in an interaction between Ala308 and Phe194. This interaction places Asn195 in a hydrogen bond with NH- group of the GlcNAc moiety and the oxy bridge of the diphospho moiety. In addition, a hydrogen bond is formed between Ser143 and NH- group of the GlcNAc moiety and between main chain NH- of Ser144 and CO- group of the GlcNAc moiety. (a) Important interactions with the GlcNAc moiety of the substrate UDP-GlcNAc are highlighted as green (polar interactions) or purple (nonpolar interactions). Tyr166 and Ser142 are hydrogen bonded to 4' hydroxyl group. This region defines the catalytic motif and is highly conserved as is Asn195. The regions defining the substrate binding site are mainly contributed by residues 209-214, 225-234 and 297-308. (b) A schematic representation of the interactions deemed most important in the substrate recognition and catalysis. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at wileyonlinelibrary.com.]
