Fig. 7.
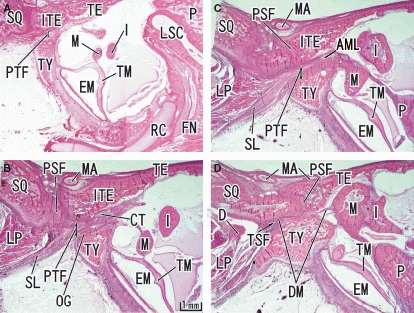
Closure of the tympanosquamosal fissure and the formation of the petrotympanic fissure seen in a 25-week human fetus. Sagittal sections. Panel A (D) is the most lateral (medial) level of the figure. The inferior process of the tegmen tympani (ITE) has descended to occupy a wedge position between the squamous part of the temporal bone (SQ) and the tympanic bone (TY). Subsequently, the petrotympanic fissure (PTF) is formed and the chorda tympani nerve (CT) and the sphenomandibular ligament (SL) passes through the fissure. AML, anterior ligament of the malleus; FN, facial nerve; LSC, lateral semicircular canal; RC, Reichert's cartilage; TSF, tympanosquamosal fissure. D, temporomandibular joint disc; DM, discomalleolar ligament; EM, external auditory meatus; I, incus; LP, lateral pterygoid muscle; M, malleus; MA, primitive maxillary artery including the middle meningeal artery; OG, os goniale; P, petrous part of the temporal bone; PSF, petrosquamosal fissure; TE, tegmen tympani of the petrous part of the temporal bone; TM, tympanic membrane.
