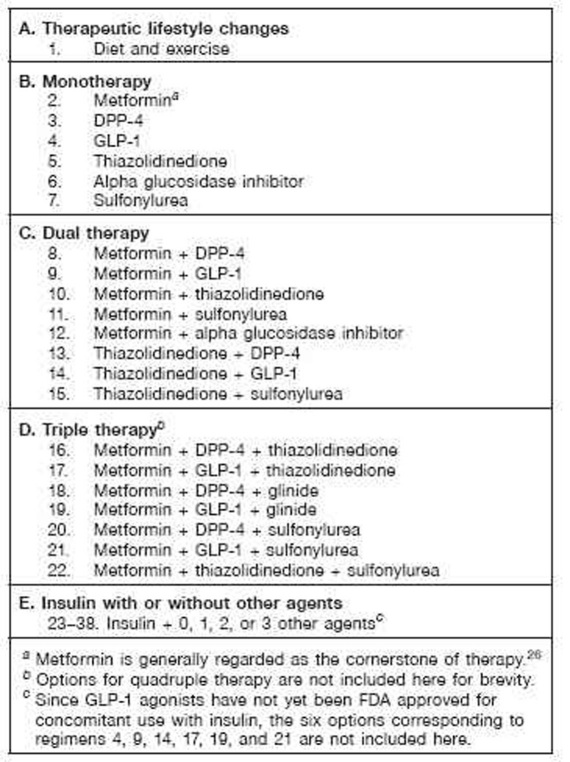
Figure 2.
Sequence of treatment regimens. Each of these medication regimens can be combined with basal insulin, creating regimens 23–38. Many more combinations are potentially available. Combinations of insulin + GLP-1 agonists have not been approved by the FDA. Combinations of insulin + thiazolidinedione may lead to excessive weight gain, fluid retention, and occasionally (2% of cases) congestive heart failure and might increase the risk of ischemic heart disease. Combinations of a sulfonylurea or glinide with insulin therapy and other agents carry an increased risk of hypoglycemia. Agents that are expected to be effective for control of PPG (glinides, DPP.-4, GLP.-1, alpha glucosidase inhibitors) would ordinarily be used with basal insulin but not with prandial, premixed, or basal.bolus insulin therapy. Sitagliptin has been approved by the FDA for use with insulin; to date, saxagliptin has not been approved for use with insulin in the United States. Approved usage varies in other countries. Exenatide has been approved for monotherapy; to date, liraglutide has not been approved for monotherapy in the United States.