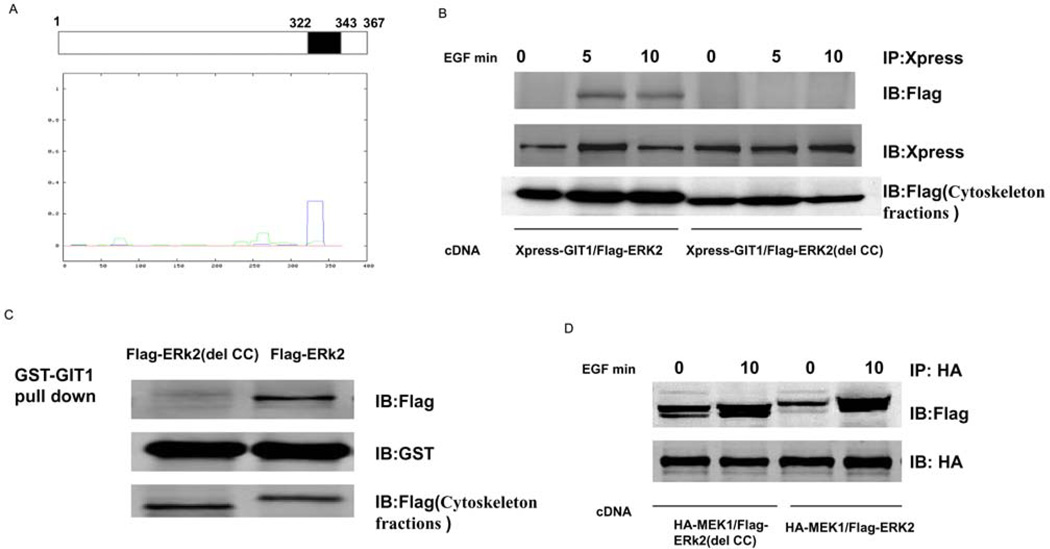
Figure 3. CC domain of ERK2 is required for association with GIT1 in cytoskeletal fractions.
(A) ERK2 sequences were analysed using the Lupas method and one major CC domain (amino acids 322–343) was found to exist in the C-terminus of ERK2. (B) HeLa cells were co-transfected with Xpress–GIT1 and FLAG–ERK2 or Xpress–GIT1 and FLAG–ERK2(del CC) for 24 h, serum-starved for 6 h, and then stimulated with EGF as indicated. The cell cytoskeletons were separated as described in the Materials and methods section. Cell cytoskeleton fractions were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Xpress antibody and probed with an anti-FLAG antibody (top panel). To confirm equal protein loading, the blot was re-probed with an anti-Xpress antibody (middle panel). Protein expression was detected by probing with an anti-FLAG antibody in cytoskeleton fractions (bottom panel). (C) GST–GIT1 was immobilized on glutathione-conjugated beads and incubated with cytoskeleton fractions from FLAG–ERK2- or FLAG–ERK2(del CC)-transfected HeLa cells. Beads were washed extensively and then immunoblotted for FLAG–ERK2 (top panel) and reprobed with an anti-GST antibody to confirm equal loading (middle panel). To confirm equal protein expression, cytoskeleton fractions were blotted with an anti-FLAG antibody (bottom panel). (D) HeLa cells were co-transfected with HA–MEK1 and FLAG–ERK2 or HA–MEK1 and FLAG–ERK2(del CC) for 24 h, serum-starved for 6 h, and then stimulated with EGF as indicated. The cell cytoskeletons were separated as described in the Materials and methods section. Cell cytoskeleton fractions were immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody and probed with an anti-FLAG antibody (top panel). To confirm equal protein loading, the blot was re-probed with an anti-HA antibody (bottom panel). These results were reproducibly obtained in three independent experiments. IB, immunoblot; IP, immunoprecipitation.