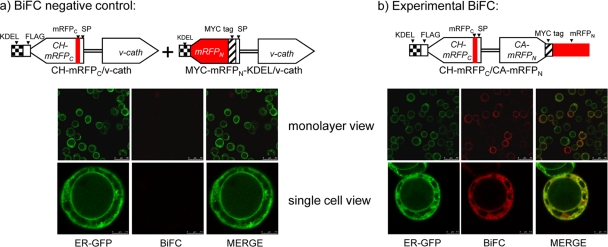
Fig. 4.
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assay. Virus constructs are shown above the corresponding fluorescence images. (a) Negative control for the BiFC assay. Cells were coinfected at an MOI of ∼100 with CH-mRFPC/v-cath, which expresses the ER-targeted CH-mRFPC fusion protein, and another virus, MYC-mRFPN-KDEL/v-cath, which expresses the ER-targeted MYC-mRFPN-KDEL protein. The MYC-mRFPN-KDEL protein was targeted to the ER by fusion to the chiA signal peptide and was modified by the addition of a C-terminal KDEL motif so that it accumulates in the ER of infected cells. Both of the BiFC negative-control viruses contain unmodified v-cath. (b) Cells were infected at an MOI of ∼100 with the CH-mRFPC/CA-mRFPN BiFC virus, which coexpresses the split-mRFP fusion proteins CH-mRFPC and CA-mRFPN, along with the ER-GFP virus to identify the ER. Virus-infected Hi5 cells were photographed at 48 hpi using confocal laser scanning microscopy. SP, chitinase signal peptide sequence.