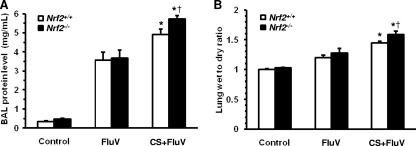
Fig. 8.
Assessment of lung permeability damage after influenza virus infection. (A) Total protein concentration in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids obtained from wild-type (Nrf2+/+) mice and Nrf2-deficient (Nrf2−/−) mice 7 days after intranasal inoculation of influenza virus (FluV) with or without exposure to cigarette smoke (CS). Control mice were inoculated with physiological saline. Data are expressed as the means ± SEM (n = 6 to 8). (B) Lung wet-to-dry weight ratio 7 days after intranasal inoculation of FluV with or without exposure to CS. Control mice were inoculated with physiological saline. Data are expressed as the means ± SEM (n = 5). *, significant difference between FluV and CS-plus-FluV groups (P < 0.05). †, significant difference between Nrf2+/+ and Nrf2−/− mice (P < 0.05).