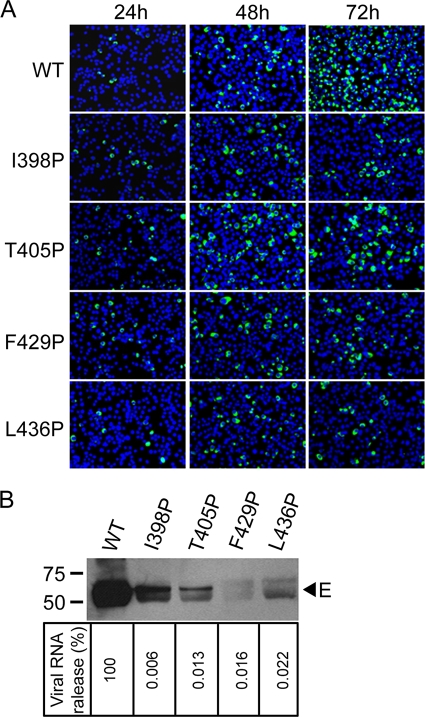
Fig. 6.
Effects of E protein stem mutations on assembly and infectivity of virions. (A) BHK-21 cells were transfected with equal amounts (10 μg) of WT and mutant genome-length RNA derived from a DENV2 infectious clone, and viral protein synthesis was analyzed by IFA at 24, 48, and 72 h posttransfection. Anti-E MAb 4G2 and Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-mouse IgG were used as primary and secondary antibodies, respectively. (B) Pellets (containing virions) derived from ultracentrifugation of culture supernatants on day 5 posttransfection were examined for E protein by Western blot analysis using anti-E MAb 4G2 (upper panel). The sizes of the molecular mass markers are shown in kDa. Viral RNA extracted from the pellets (containing virions) were quantified by real-time RT-PCR; the relative amount of viral RNA of each mutant to that of WT virus (100%) is shown (lower panel). Data are means of duplicate experiments.