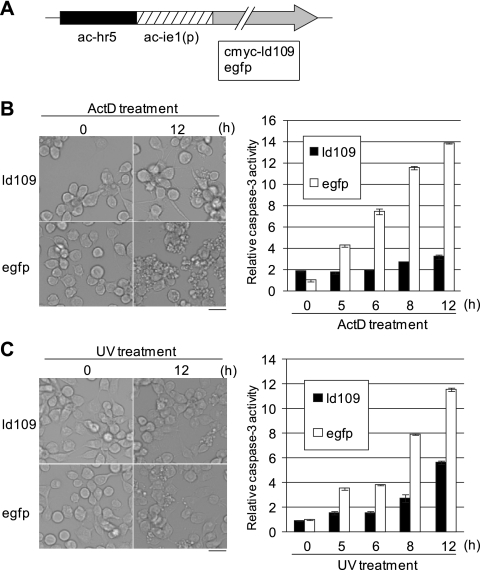
Fig. 4.
Antiapoptotic activity of Ld109 against apoptosis of Ld652Y cells induced by exposure to actinomycin D and UV. (A) Schematic representation of pIE1-2/cmyc-ld109 and pIE1-2/egfp. (B) Antiapoptotic activity of Ld109 against actinomycin D-treated cells. Ld652Y cells were transfected with 1 μg of pIE1-2/cmyc-ld109 and pIE1-2/egfp. Forty-eight h posttransfection, they were treated with TC100 medium containing 0.5 μg/ml actinomycin D. The cells were examined for apoptosis under the microscope (left), and caspase-3-like protease activity was determined at the indicated times after actinomycin D treatment (right). (C) Antiapoptotic activity of Ld109 against apoptosis induced by UV irradiation. The Ld652Y cells were transfected with 1 μg of pIE1-2/cmyc-ld109 and pIE1-2/egfp, and at 48 h posttransfection, they were exposed to UV (254 nm) irradiation at 430 μW/cm2 for 30 s by using a UVGL-58 UV lamp (Ultra-Violet Products). These cells were examined for apoptosis and caspase-3-like protease activity as described for panel B. The caspase-3-like protease activities were determined by using Ac-DEVD-AMC (N-acetyl-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-7-amino-4-methylcoumarin) as the substrate and are presented as the ratios to the activity of mock-treated cells at 0 h posttreatment (48 h posttransfection). The scale bars in the left panels indicate 30 μm. The error bars in the right panels indicate standard deviations of averages from three determinations.