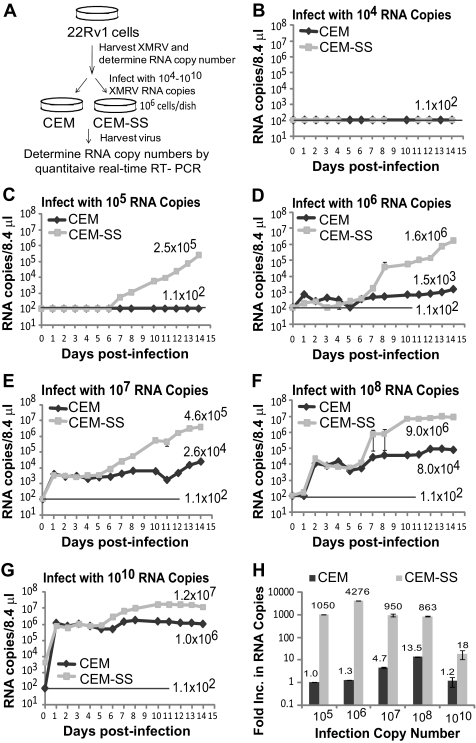
Fig. 1.
Replication of XMRV in CEM and CEM-SS cells. (A) Schematic overview of the experimental protocol. Supernatant containing XMRV was harvested from 22Rv1 cells, and XMRV RNA copies in the supernatant were determined by quantitative real-time RT-PCR using primers and a probe for a region of XMRV env. Culture supernatants containing different amounts of XMRV RNA copies were then used to infect 1 × 106 CEM or CEM-SS cells. At 6 h postinfection, cells were extensively washed, and culture supernatants were harvested every day from days 0 to 14. XMRV RNA copy numbers were determined by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. (B to G) Replication kinetics of XMRV 22Rvl in CEM and CEM-SS cells infected with 22Rv1 culture supernatant containing 104 XMRV RNA copies (B), 105 XMRV RNA copies (C), 106 XMRV RNA copies (D), 107 XMRV RNA copies (E), 108 XMRV RNA copies (F), or 1010 XMRV RNA copies (G). The viral RNA in the supernatant of infected cells was isolated, and XMRV RNA was detected by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. The results are plotted as copies of viral XMRV RNA per 8.4 μl of culture supernatant of infected cells. The detection limit for quantitative RT-PCR was 1.1 × 102 copies/8.4 μl (indicated as a solid line). A representative experiment from two independent experiments is shown. Error bars indicate standard deviations. (H) Determination of increases in viral RNA copies in CEM and CEM-SS cells 14 days postinfection. The increase in viral RNA copies produced from CEM and CEM-SS cells infected with different amounts of 22Rvl XMRV are shown in panels B to G. The average number of RNA copies per 8.4 μl for days 12 to 14 was divided by the average number of RNA copies per 8.4 μl from days 1 to 3.