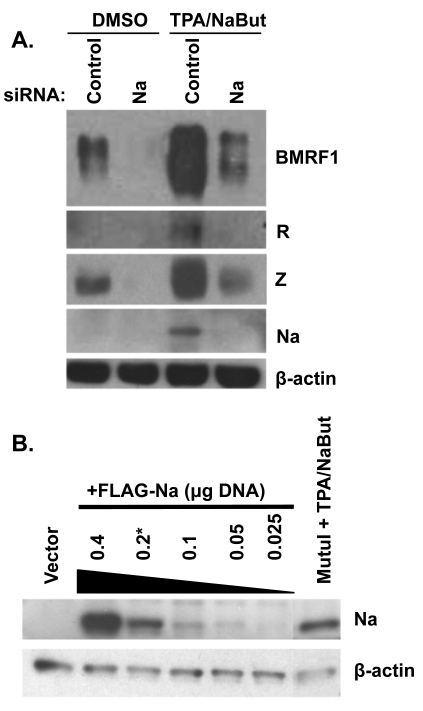
Fig. 2.
Knockdown of Na inhibits lytic protein expression. (A) CNE-2 Akata cells were transfected with siRNAs targeting control or Na sequences. Cells were then treated with either dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or TPA (20 ng/ml) plus sodium butyrate (3 mM; NaBut). Cell lysates were harvested 48 h after induction, and immunoblot analysis was performed using antibodies against BMRF1, Na, R, Z, and β-actin. (B) CNE2-Akata cells were transfected with various amounts of the FLAG-Na vector as indicated (in a 12-well plate). At 48 h posttransfection, an immunoblot assay was performed (using an anti-Na antibody) to compare the level of Na expressed in the transfected CNE-Akata cells versus that expressed from the endogenous viral genome in MutuI cells treated with TPA/NaBut. β-Actin levels were examined as a protein loading control.