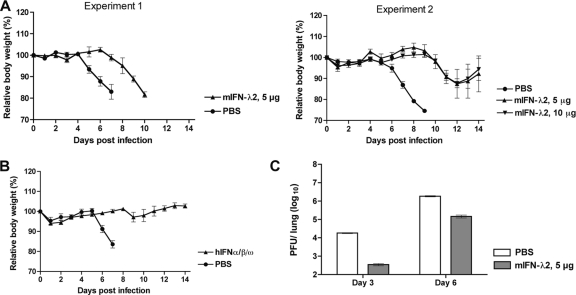
Fig. 9.
Protective capacity of exogenous type I and type III IFN in a lethal PVM infection. C57BL/6 mice in groups of five were treated intranasally with 5 or 10 μg of murine IFN-λ2 (A), 106 units of a mixture of IFN-α/β/ω (B), or PBS (A and B) with a volume of 100 μl. Eight hours later, the mice were infected intranasally with 5,000 PFU of wild-type PVM in a volume of 80 μl. The mice were observed closely, and body weight was monitored daily. (C) To determine the virus load of mice pretreated with IFN-λ2, C57BL/6 mice in groups of 10 were treated as described for panel A; five mice of each group were sacrificed on day 3 and day 6 after infection, the lungs were removed and homogenized, and viral titers were determined by plaque assay.