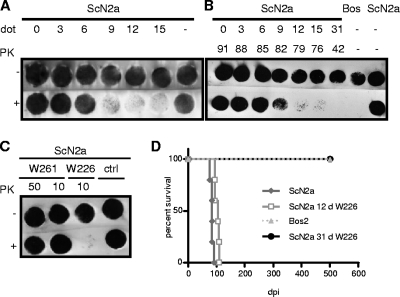
Fig. 5.
Cell blot immunoassays of scrapie-infected and antibody-treated ScN2a cells tested for the presence of the pathological prion protein PrPSc by PK digestion and immunostaining with MAb W226. (A) Reduction of the PrPSc load in ScN2a cells after various days of treatment (dot) with MAb W226. (B) Reduction and absence of PrPSc in ScN2a cells after treatment with W226 for the indicated numbers of days (0 to 31 days) (upper row) and following incubation for various periods in the absence of the antibody (42 to 92 days) (lower row). (C) Treatment of scrapie-infected ScN2a cells with the PrPSc-specific MAb W261 did not alter the amount of PrPSc. ScN2a cells were cultured with the indicated amounts of MAb W261 for 104 days and were subsequently tested for the presence of the pathological prion protein PrPSc. Analysis revealed no differences between proteinase K-treated and untreated cells, indicating that cultivation with MAb W261 had no influence on the PrPSc level in ScN2a cells. ctrl, control. (D) Absence of disease transmission to tga20 mice from ScN2a cells treated for 31 days with W226. Cell blotting was performed as described previously (8).