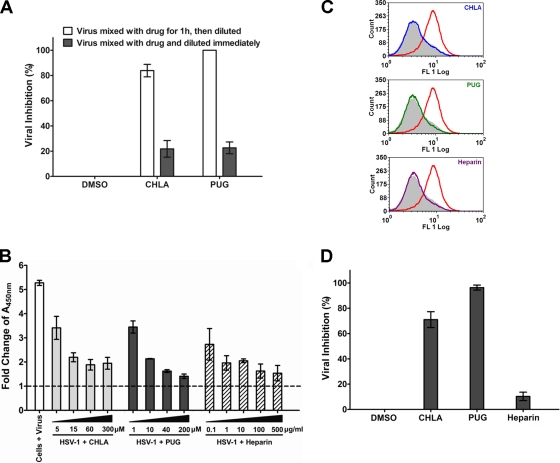
Fig. 5.
CHLA and PUG inhibit HSV-1 entry by inactivating viral particles and preventing virus binding and internalization into A549 cells. (A) Viral inactivation assay. HSV-1 (104 PFU/ml) was mixed with CHLA (60 μM) or PUG (40 μM) for 1 h at 37°C and then diluted 50-fold (final virus concentration, 50 PFU/well) before infecting A549 cells. As a control, the same amount of virus was also mixed with the tannin, but diluted immediately and applied to the A549 cells. After a 48-h incubation period, viral plaques were stained and counted. DMSO (0.1%) was included as a negative control. The data shown are means ± the SEM of three independent experiments with each treatment performed in duplicate. (B) Viral attachment analysis using ELISA. Adherent A549 cell monolayers in 96-well plates were prechilled at 4°C for 1 h and then inoculated with HSV-1 (MOI = 5) in the presence of CHLA, PUG, or the DMSO (1%) and heparin controls at various concentrations for another 3 h at 4°C. Wells were washed to remove unadsorbed virus, subsequently fixed with 4% PFA, and then blocked with 5% BSA. ELISA was performed with a primary polyclonal rabbit anti-HSV-1 antibody (1:7,500) and a secondary goat anti-rabbit IgG conjugated with HRP (1:100,000), followed by development with TMB substrate and reaction termination with 1 M H3PO4. The absorbance was immediately determined at 450 nm. Values are expressed as the fold change of absorbance relative to the mock infection control (cells + 1% DMSO), which is indicated by the dashed line. The data shown are means ± the SEM of three independent experiments with each treatment performed in triplicate. (C) Viral binding assay using flow cytometry analysis. Dissociated A549 cells were infected with HSV-1 (MOI = 1) in the presence or absence of 60 μM CHLA or 40 μM PUG for 3 h at 4°C. Cells were then washed, blocked, and stained with FITC-conjugated polyclonal rabbit anti-HSV-1 antibody (1:500). Stained samples were washed and fixed with 1% PFA before being subjected to standard flow cytometry analysis. DMSO (0.1%) was used as a negative control, and heparin (100 μg/ml) was included as a positive control. Color indication for different treatments: gray, mock + DMSO; red, HSV-1 + DMSO; blue, HSV-1 + CHLA; green, HSV-1 + PUG; and purple, HSV-1 + heparin. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments. (D) Viral penetration analysis by plaque assay. A549 cells were prechilled at 4°C for 1 h before inoculation with HSV-1 (100 PFU/well) for 3 h at 4°C. The cells were then treated in the presence or absence of CHLA (60 μM), PUG (40 μM), or heparin (100 μg/ml) and further incubated for an additional 20 min with the temperature shifted to 37°C to facilitate viral penetration. At the end of the incubation, extracellular virus was inactivated by citrate buffer (pH 3.0) for 1 min and then washed with PBS twice before overlaying with medium. After 48 h of incubation at 37°C, viral plaques were stained and counted. DMSO (0.1%) was included as a negative control. The data shown are means ± the SEM of three independent experiments with each treatment performed in duplicate.