Figure 7.
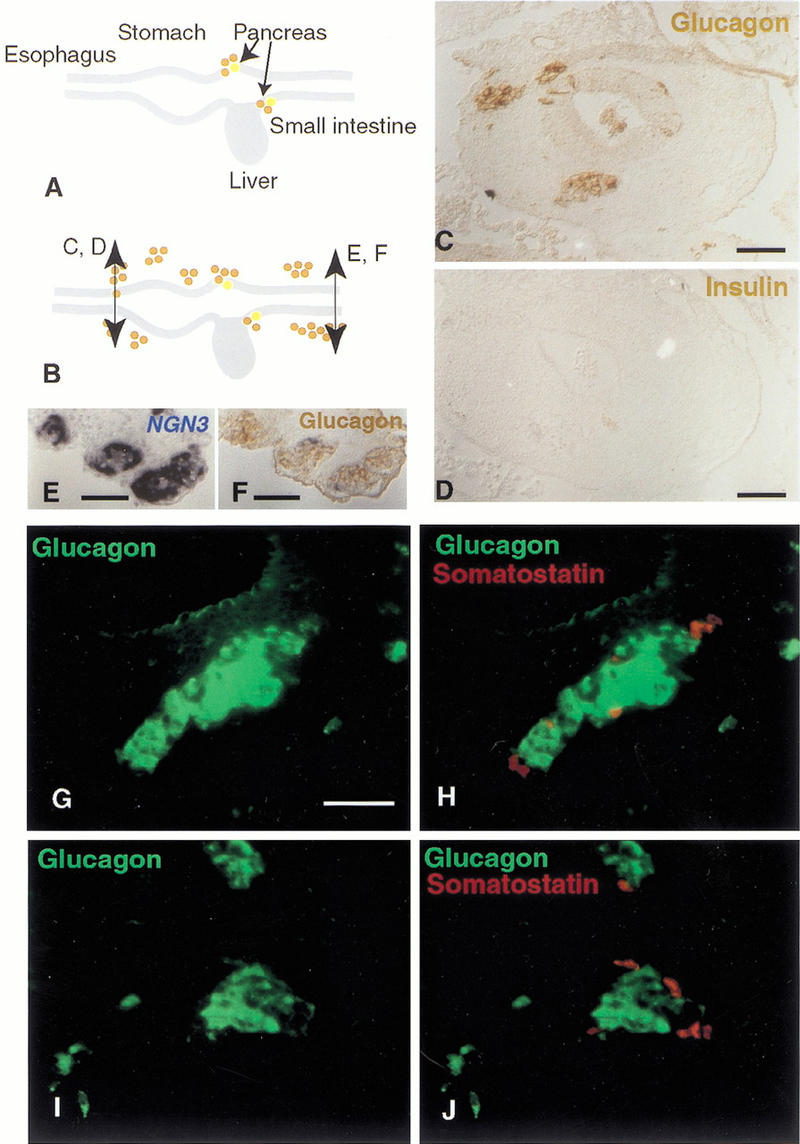
ngn3 induces glucagon- and somatostatin-islet formation from the esophagus to the yolk stalk. (A) Glucagon (brown) and insulin (yellow) are synthesized in cells of the E4 pancreatic buds but not in other cells of the gut epithelium at that stage. (B) Cells overexpressing ngn3 from the stomach to the yolk stalk start expressing glucagon, as shown in brown by immunohistochemistry in the stomach (C) and yolk stalk (F). (D) A section adjacent to C shows that insulin is not present in these cells. (E) A section adjacent to F shows the location of ngn3-positive cells, labeled in blue after in situ hybridization. Most glucagon-positive cells emigrate from the epithelium after 48 h and aggregate into islets (B,C,F) of about 10–100 cells. Glucagon immunostaining alone (green; G,I) or overlayed with somatostatin immunostaining (red; H,J) of typical islets close to the epithelium in the region of the jejunum. Somatostatin-positive cells are distinct from glucagon-positive cells and are located at the periphery of the islet. Bars, 50 μm.
