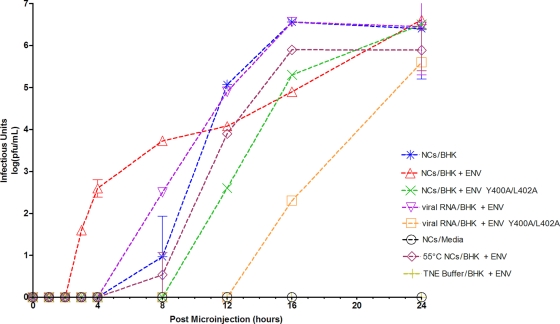
Fig. 1.
Detection of infectious unit release after microinjection of cells with nucleocapsids. Nucleocapsids (NCs) or viral RNAs were microinjected into the cell type as indicated. Cells expressed wild-type envelope proteins containing an RFP:E2 fusion (BHK + ENV), the envelope proteins containing the E2 Y400A/L402A mutations in addition to the RFP:E2 fusion (BHK + ENV Y400A/L402A), or no viral envelope proteins (BHK). In some cases, NCs were heat shocked at 55°C for 3 min immediately before microinjection. At the time points indicated on the x axis, media were removed from cells and replaced with fresh media. Media were assayed by plaque assay for the presence of infectious units, and the titer [log(PFU/ml)] was plotted as a function of time postmicroinjection. Microinjection of NC buffer (TNE) into BHK cells expressing the envelope proteins represented a mock sample, and NCs microinjected directly into the media provided an additional negative control.