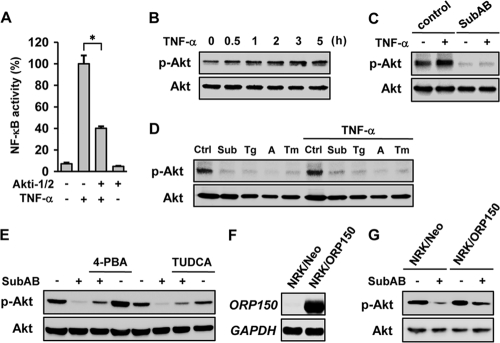
Fig. 4.
Suppression of Akt and consequent inhibition of NF-κB activation by SubAB. (A) NRK/NFκB-Luc cells were treated with or without TNF-α in the absence or presence of 10 μM Akti-1/2 and subjected to luciferase assay. (B) NRK-52E cells were treated with TNF-α for up to 5 h and subjected to Western blot analysis of phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt) and total Akt protein (Akt). (C) Cells were pretreated with or without SubAB, exposed to TNF-α, and subjected to Western blot analysis. (D) Cells were treated with SubAB (Sub), thapsigargin (Tg; 500 nM), A23187 (A; 2 μM), or tunicamycin (Tm; 1 μg/ml) for 24 h, treated with or without TNF-α for 5 h, and subjected to Western blot analysis. Ctrl, untreated control. (E) Cells were treated with SubAB in the absence or presence of chemical chaperone 4-PBA (1 mM) or TUDCA (1 mM), and the level of phosphorylated Akt was evaluated. (F) Cells were stably transfected with ORP150. Mock transfected cells (NRK/Neo) and established transfectants (NRK/ORP150) were subjected to Northern blot analysis of ORP150. (G) NRK/Neo cells and NRK/ORP150 cells were treated with SubAB, and phosphorylated Akt was examined.