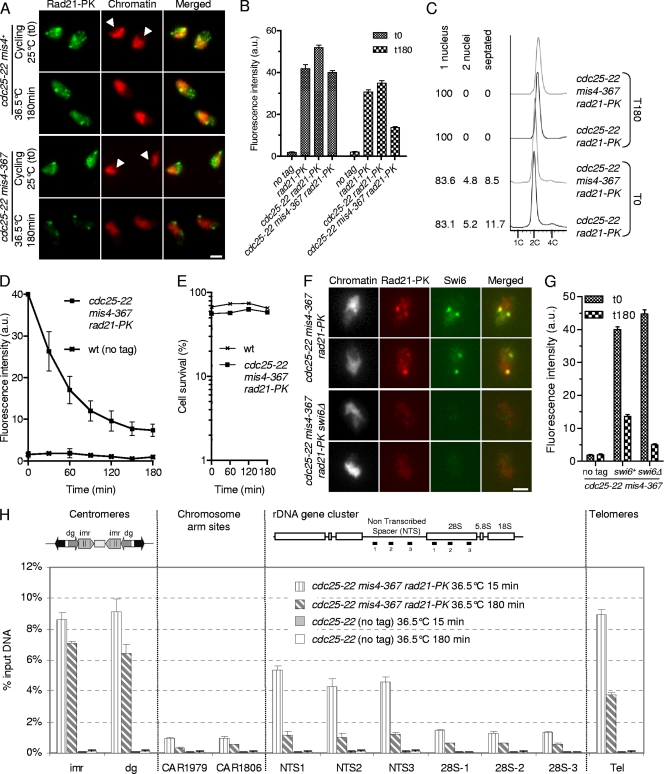
Fig. 1.
Characterization of the cohesin fraction stably bound to postreplicative chromosomes. (A to D) A fraction of Rad21 persists on G2 chromatin after inactivation of the cohesin-loading machinery. Cycling cells were shifted to 36.5°C to shut off cohesin loading (mis4-367) while keeping the cells in G2 (cdc25-22). Chromatin-bound Rad21-9PK was measured at the indicated time points by nuclear spreading and immunofluorescence using anti-PK antibodies. (A) Images of nuclear spreads showing chromatin-bound Rad21-9PK before (cycling) and 180 min after the temperature shift. Chromatin was counterstained with DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole). The arrowheads point to the nucleoli, which are located in the area of the nucleus unstained by DAPI. Bar, 2.5 μm. (B) Rad21-9PK fluorescence intensity was measured for 50 to 100 nuclei for each sample. Error bars, 95% confidence intervals of the mean. a.u., arbitrary units. (C) Analysis of the cell cycle stage confirmed that most cells (>80%) were in the G2 phase before the temperature shift and remained in G2 throughout the experiment. The positions of cells within the cell cycle were analyzed by DNA content analysis. DAPI and calcofluor staining were used to score mononucleate, binucleate, and septated cells. (D) Kinetics of Rad21 dissociation from chromatin. The data presented are the means of 10 independent experiments. The error bars represent standard deviations (SD). wt, wild type. (E) Cell survival remained high during the course of the experiment. Cells were withdrawn at the indicated time points and plated at the permissive temperature to determine the number of viable cells. (F) The major foci of cohesin in the stable fraction colocalize with Swi6. Cells were treated as in panel A, and nuclear spreads were prepared 180 min after the temperature shift, at which time only the stable cohesin fraction is retained on chromatin. Bar, 2.5 μm. (G) The stable cohesin fraction is reduced in cells lacking Swi6. The Rad21-9PK fluorescence intensity was measured for 50 to 100 nuclei for each sample. Error bars, 95% confidence intervals of the mean. (H) Rad21 ChIP assay showing the distribution of the labile and stable cohesin fractions along the chromosomes. Cells were cultured as in panel A and processed for ChIP just after (15 min) and 180 min after the temperature shift. Rad21 enrichment was measured at centromeres (imr and dg), at two chromosome arm sites (CAR1806 and CAR1979), within the rDNA gene cluster (NTS and 28S), and at telomeres (Tel). Rad21 enrichment was calculated from duplicate samples. The error bars indicate SD.