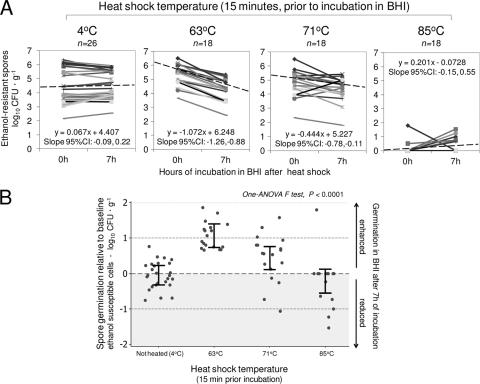
Fig. 4.
Effect of heat shock on immediate cultivability and subsequent germination of C. difficile spores determined by enumeration of ethanol-resistant cells before and after 7 h of incubation in BHI. (A) Line plots represent paired enumeration of heat-shocked and nonheated individual spore replicas. Linear equations and extended dashed lines represent average effects (slopes). The highest and steepest dashed line (63°C) indicates immediate enhanced cultivability and subsequently increased spore germination. The panel for 85°C shows immediate inhibition and subsequent increased cultivability. (B) Spore germination relative to baseline. Normalized paired differences (before and after BHI incubation). Heat shock with 63 and 71°C enhanced germination in spores that otherwise would have remained dormant after an additional 7 h of incubation in BHI and 72 h in blood agar at 37°C (here referred to as superdormant spores). Dots represent average difference per replica; means ± 95% CI (see also Table S1 in the supplemental material).