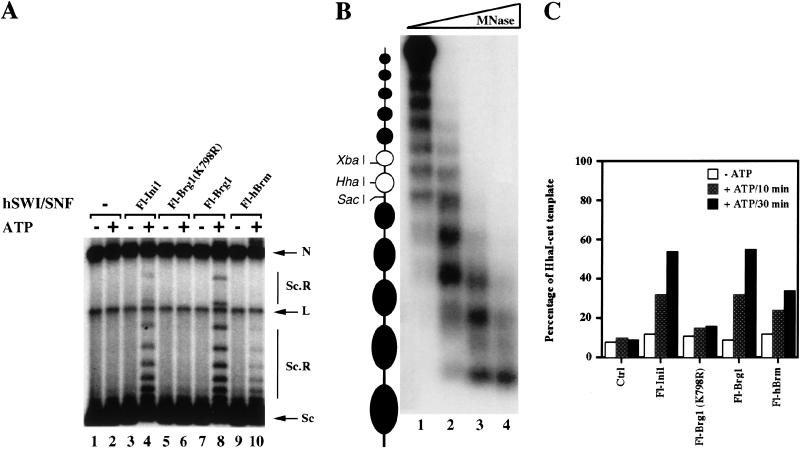
Figure 3.
Disruption of polynucleosomal templates. (A) Brg1 and hBrm complexes can alter the topology of highly negatively supercoiled chromatin templates. Approximately 144 ng (2.88 nM) of affinity-purified Fl-Ini1 complexes (lanes 3,4), mutant Fl-Brg1 (lanes 5,6), wild-type Fl-Brg1 (lanes 7,8), and Fl-hBrm (lanes 9,10) was incubated with nucleosome-assembled plasmid DNA in the absence or presence of ATP as indicated. (Lanes 1,2) Assembled templates without Brg1 and hBrm complexes. (N) Nicked closed circular DNA; (L) linear DNA; (Sc) supercoiled DNA; (Sc.R) less supercoiled and relaxed DNA. (B) Analysis of the 5S polynucleosomal array. To determine the extent of assembly of the 5S array, increasing amounts of MNase (lane 1, 1 mU; lane 2, 10 mU; lane 3, 100 mU; lane 4, 1U) were added to 2 ng of assembled template, and the 5S DNA was detected by Southern blotting as described in Materials and Methods. (C) Brg1 and hBrm complexes can increase restriction enzyme accessibility. Equal amounts (144 ng, or 2.88 nM) of affinity-purified Brg1 and hBrm complexes were incubated with 6 ng (0.14 nM) of 5S nucleosomal arrays. After either 10 or 30 min at 30°C, HhaI was added, and the reactions were incubated for an additional 60 min at 30°C. The percentage of HhaI-cut template represents the ratio of cut DNA to total amount of template.