Fig. 9.
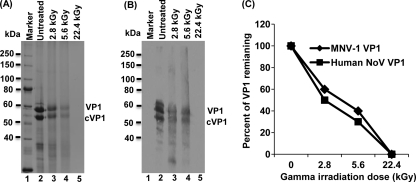
Gamma irradiation degrades the capsid protein of human norovirus. (A) Visualization of human norovirus capsid protein by 12% SDS-PAGE. The purified VLPs were irradiated with 2.8, 5.6, and 22.4 kGy. Total viral proteins were analyzed by 12% SDS-PAGE, followed by Coomassie staining. VP1 = human norovirus capsid protein; cVP1 = cleaved VP1 protein. (B) Western blot analysis of human norovirus VP1 protein. Samples identical to those shown in panel A were separated by SDS-PAGE and subjected to Western blotting using a polyclonal antibody against VP1 protein. (C) Comparison of the stability levels of the capsid proteins of MNV-1 and human norovirus after exposure to gamma irradiation. Two micrograms of MNV-1 and human norovirus VLPs was treated with 2.8, 5.6, and 22.4 kGy. Total proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, followed by Coomassie staining. The remaining proteins from gamma irradiation were quantified by ImageQuant TL software. Data points were averages of three replicates.