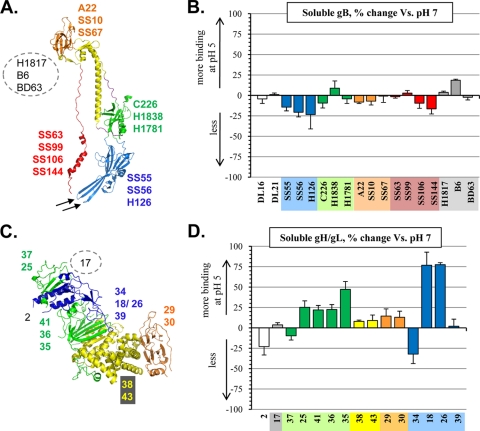
Fig. 4.
(A) Crystal structure of the soluble gB protomer (residues 111 to 725). Structural domains are indicated by color: domain I, blue; II, green; III, yellow; IV, orange; and V, red. MAbs used in this study are indicated and color coded according to the domain in which their epitope lies. The epitopes of gB MAbs H1817, B6, and BD63 are found within the unsolved N-terminal domain and are shown within a gray dotted circle. Two arrows point to the fusion loops. (B) ELISA showing the percent change of MAb binding to various gB epitopes in the soluble protein at pH 5 versus pH 7. The gB MAbs tested are shown along the x axis, color coded according to the domain in which their epitopes lie. MAbs DL16 and DL21 (shown in white) have conformation-dependent epitopes that have not been localized onto the structure. An average of at least three independent experiments is show. Error bars represent standard error. No change in MAb binding, value of zero (center line, x axis); increase in MAb binding at pH 5, positive value (above the center line); decrease in MAb binding at pH 5, negative value (below the center line). (C) Crystal structure of soluble gH/gL (gH residues 48 to 797 and gL residues 24 to 203). Structural domains are indicated by color: domain H1, green; H2, yellow; H3, orange; and gL, blue. Numbers representing gH/gL MAbs (CHL series) used in this study are shown beside the ribbon diagram, color coded according to the domain in which their epitope lies. The epitope of MAb CHL17 is found within the unsolved N-terminal domain, shown within a gray dotted circle. The epitope of CHL2 is discontinuous and requires both gH and gL; however, we have isolated a MAb-resistant mutant with a change to gH amino acid 116 (13). This residue is found in domain H1, so we have labeled the CHL2 epitope in this area of the structure. (D) ELISA showing the percent change of MAb binding to various gH/gL epitopes at pH 5 versus pH 7 in the soluble protein complex. Graph is set up as described in panel B. MAb CHL2 has a conformation-dependent epitope that potentially includes residues of both gL and domain H1 of gH; therefore, it is represented as a white bar in our ELISA graph.