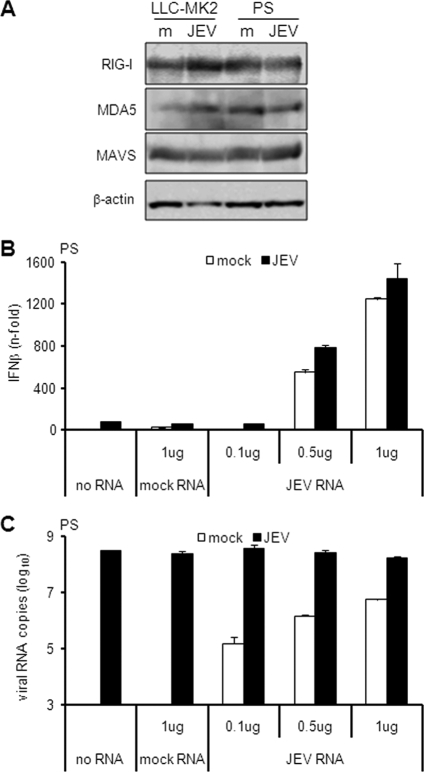
Fig. 5.
Effect of JEV on the IFN activation pathway. (A) LLC-MK2 or PS cells were mock treated (m) or infected with JEV at an MOI of 1 for 24 h. Cellular extracts were subjected to immunoblotting for the proteins indicated on the left, with β-actin as the internal control. (B and C) PS cells were mock treated or infected with JEV at an MOI of 1 for 18 h, and then the indicated amounts of total RNA from mock-treated or JEV-infected LLC-MK2 cells were transfected for another 6 h. IFN activation (B) and viral RNA titers (C) were measured by real-time quantitative RT-PCR. The results for IFN-β mRNA are expressed as the fold increase over mock-treated cells. The results for JEV RNA are expressed as the log10 number of RNA copies per 1 μg total RNA. The values were normalized to β-actin, and the error bars indicate standard deviations of the means.