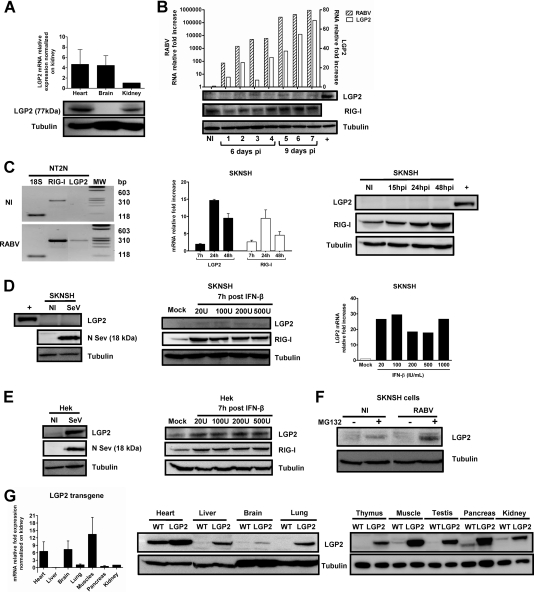
Fig. 2.
LGP2 protein expression is strongly restricted in mouse brain and human neuronal cells because of its degradation. (A) LGP2 mRNA (top) and LGP2 protein (bottom) expression in the hearts, brains, and kidneys of WT mice was quantified by qRT-PCR and normalized to the LGP2 mRNA level in the kidney (value taken as 1) or determined by Western blotting normalized to tubulin. qRT-PCR data are presented as means and SEM (n = 4). (B) Seven RABV-infected mice were sacrificed at different times after virus injection (the first 4 mice were sacrificed at day 6 p.i., and the last 4 were sacrificed at day 9 p.i.). Brains were separated into two parts. One half of the brain was used for qRT-PCR, and the other was used for Western blotting. RABV N and endogenous mouse LGP2 mRNAs in the brains of RABV-infected WT mice or noninfected (NI) animals were quantified by qRT-PCR (top). LGP2, RIG-I (used as a control protein), and tubulin (used as a gel loading control) protein expression in the brains of sacrificed mice was monitored using Western blotting (bottom panels). The positive control (+) is LGP2 expression in a WT heart lysate. (C) LGP2 and RIG-I expression in human postmitotic neurons (NT2N) and neuroblastoma SKNSH cells after RABV infection (24 h for NT2N cells and 7, 15, 24, and 48 h for SKNSH cells) or no infection (NI) was measured by RT-PCR (NT2N cells; 18S rRNA was used as an internal control) and by qRT-PCR (SKNSH cells; values were normalized to the NI control, with a value of 1). Proteins were detected by Western blotting for SKNSH cells, with a heart lysate as a positive control (+) for LGP2 protein (n = 3). (D) LGP2 expression in SKNSH cells was measured 24 h after SeV infection by Western blotting (left; SeV N protein expression was used as a control for infection) and 7 h after treatment with increasing doses of IFN-β (20, 100, 200, and 500 IU/ml) by Western blotting (central panel; RIG-I expression was used as a control for IFN-β treatment efficiency) and qRT-PCR (normalized with the mock value, taken as 1). (E) LGP2 expression in nonneuronal cells (Hek) was measured by Western blotting 24 h after SeV infection (left) and 7 h after treatment with increasing IFN-β doses (right). SeV N protein expression was used as a control for infection, RIG-I was used as a control for IFN-β treatment efficacy, and tubulin was used as a control for protein loading. (F) Western blotting showing the effect of MG132 treatment (10 μM) on LGP2 expression in NI and RABV-infected SKNSH cells. (G) LGP2 expression in the brains of LGP2 TG mice. LGP2 protein and LGP2 mRNA expression was analyzed by qRT-PCR normalized to LGP2 transgenic mRNA levels in the kidney (n = 4) (left) (data are presented as means and SEM) and by Western blotting with lysates of hearts, livers, brains, lungs, thymuses, muscles, testes, pancreases, and kidneys of LGP2 TG (LGP2) and WT mice (right). Tubulin was used as a control of protein loading.