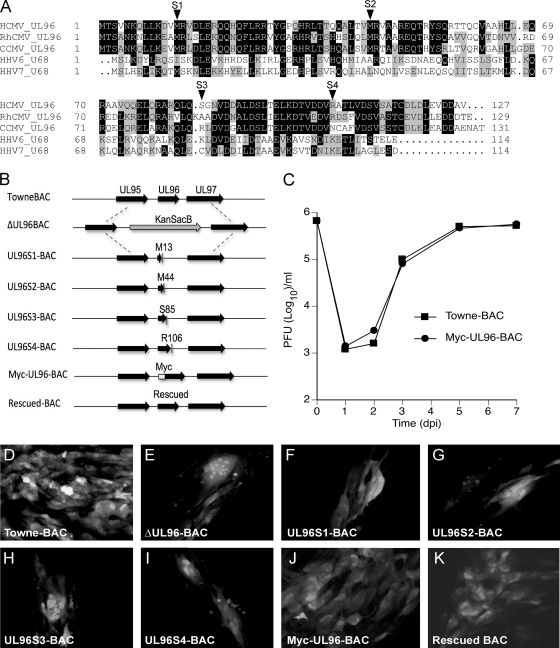
Fig. 1.
pUL96 is a betaherpesvirus conserved protein critical for HCMV growth in cell culture. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of pUL96 homologs from HCMV (YP_081543), RhCMV (YP_068222), CCMV (AAM00734), HHV6 (CAA58360), and HHV7 (YP_073808). Identical amino acids (black) and similar amino acids (gray) are highlighted. (B) Schematic of the UL95-UL97 region in TowneBAC (top line) with other bacmid constructs shown below. ΔUL96BAC is depicted with a KanSacB insert replacing UL96, UL96S1-BAC through UL96S4-BAC are depicted with the positions of amino acids (M13, M44, S85, and R106) that were replaced with novel termination codons to prematurely terminate UL96, Myc-UL96-BAC is depicted with the position of an amino-terminal epitope tag on UL96, and rescued BAC, constructed from the ΔUL96BAC, is depicted with repaired UL96. (C) Single-step growth curves of TowneBAC and Myc-UL96-BAC viruses. HF were infected (MOI of 3.0), total viruses (cells plus medium) were harvested at the indicated times postinfection, and titers were determined on HF monolayers. The viral titers represent the averages of triplicate experiments, and standard errors are within symbols. The data point at 0 dpi indicates the input virus dose. (D to K) Typical eGFP+ plaque phenotypes of the indicated BAC constructs at 10 dpt in HF. Original magnification, ×400.