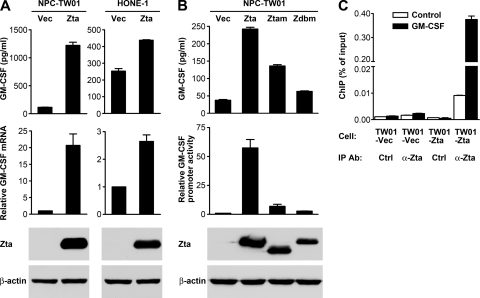
Fig. 4.
Zta upregulates GM-CSF expression in NPC cells. (A) NPC-TW01 and HONE-1 cells were transfected with a vector plasmid (Vec) or a Zta-expressing plasmid (Zta). GM-CSF concentrations in the cell culture supernatants were measured by using ELISA. GM-CSF mRNA was measured by quantitative RT-PCR. Intracellular Zta and β-actin proteins were detected by an immunoblotting assay. (B) NPC-TW01 cells were transfected with a vector plasmid or a plasmid expressing wild-type Zta, a transactivation-impaired Zta mutant (Ztam), or a DNA-binding-defective Zta mutant (Zdbm). GM-CSF concentrations in the cell culture supernatants were measured by using ELISA. Intracellular Zta and β-actin proteins were detected by an immunoblotting assay. These effector plasmids were also cotransfected with a GM-CSF reporter plasmid into NPC-TW01 cells, and their effects on GM-CSF promoter activity were examined by using a luciferase reporter gene assay. (C) NPC-TW01 cells were transfected with a vector plasmid (TW01-Vec) or a Zta-expressing plasmid (TW01-Zta) and then subjected to a ChIP assay. An anti-Zta antibody (α-Zta) and a control antibody (Ctrl) were used as the immunoprecipitating antibodies (IP Ab). The amounts of GM-CSF promoter DNA (black bars) and control DNA (white bars) in the immunoprecipitants were quantified by using real-time PCR and expressed as “percentage of input.”