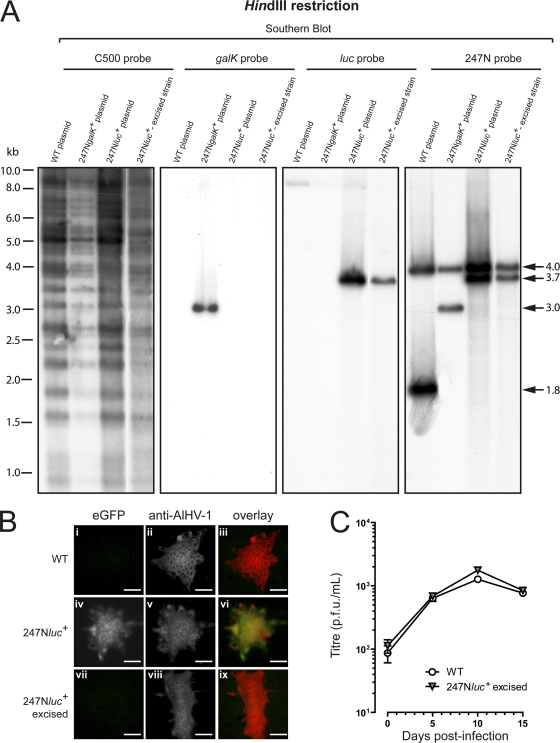
Fig. 2.
Characterization of the 247Nluc+ plasmid and derived recombinant strain. (A) The WT, 247NgalK+, and 247Nluc+ plasmids and the DNA extracts of cells infected with the 247Nluc+-excised strain were analyzed by HindIII restriction and further tested by Southern blotting using the indicated probes. (B) Epifluorescence analysis of AlHV-1 syncytia. MDBK cells were infected (MOI, 10−4 PFU/cell) with the WT (i to iii), 247Nluc+ (iv to vi), and 247Nluc+-excised (vii to ix) strains. The horizontal rows represent analyses of the same syncytium. Images i, iv, and vii and images ii, v, and viii were analyzed for eGFP and Alexa Fluor 568 fluorescent emissions, respectively. The merged eGFP and Alexa signals are shown in images iii, vi, and ix. Original magnification, ×200; bar, 50 μm. (C) Replication kinetics of the C500 BAC 247Nluc+-excised strain were compared with those of the parental AlHV-1 C500 WT strain as described in Materials and Methods. The data presented are the means ± standard deviations (SD) of results from triplicate measurements. Statistical analyses by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Bonferroni's posttest.