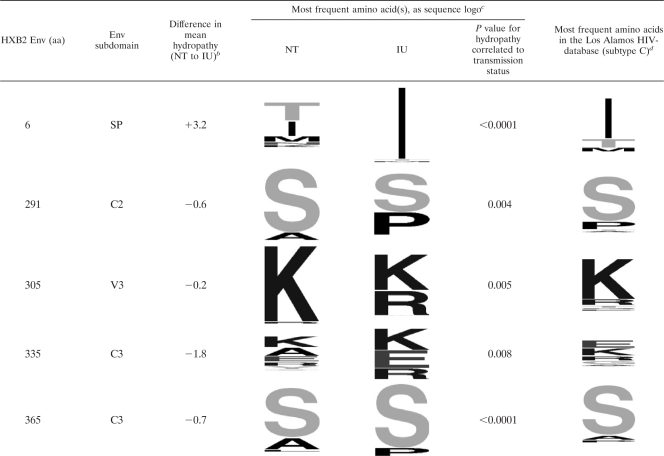
Table 3.
Changes in hydropathy at several Env positions are correlated with in utero mother-to-child transmissiona
Shown are the individual amino acid (aa) positions, according to HXB2 numbering, and the corresponding subdomain of Env where that position is found (SP, signal peptide; V, variable; C, conserved).
Difference in mean hydropathy indicates the difference in the bootstrap mean estimate of the Kyte-Doolittle hydropathy at the position, stratified by transmission status. A positive value indicates more hydrophobic residues in in utero mother-to-child transmission (IU); a negative value indicates more hydrophobic residues in the nontransmitters (NT).
The most frequent amino acids are displayed using sequence logo, where the size of the letter is proportional to its frequency. The P values represent the raw (not multiple-hypothesis-corrected) correlation between hydropathy at the position and the transmission status.
The most frequent amino acids in 757 HIV-1 subtype C sequences in the Los Alamos HIV database.