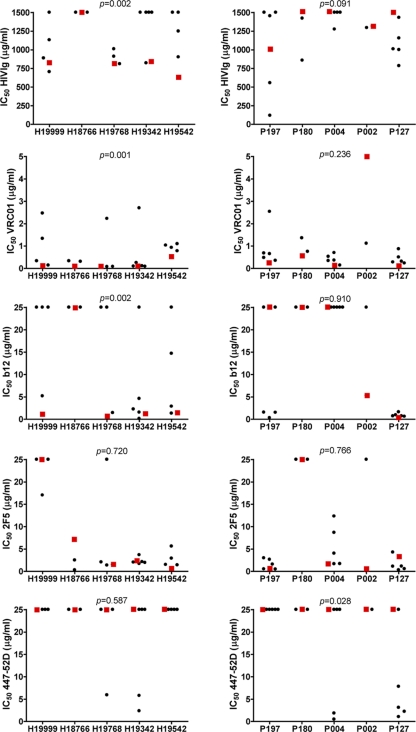
Fig. 2.
Neutralization sensitivities of the chimeric NL4-3/Env viruses in which the V1V2 loop was exchanged between viruses from historical and contemporary seroconverters. The chimeric NL4-3/Env viruses consisting of Env of an HIV-1 variant from a historical seroconverter with the V1V2 region of an HIV variant from a contemporary seroconverter are depicted in the left panels, and the chimeric NL4-3/Env viruses consisting of Env of an HIV-1 variant from a contemporary seroconverter with the V1V2 region of an HIV variant from a historical seroconverter are depicted in the right panels. IC50s, determined by linear regression, are indicated for HIVIG and MAbs VRC01, b12, 2F5, and 447-52D (from top to bottom), with a red square representing the original wild-type NL4-3/Env virus and each black circle representing a corresponding chimeric NL4-3/Env virus in which the V1V2 loop has been exchanged. Differences in neutralization sensitivities to HIVIG and MAbs of the V1V2 exchange chimeras compared to the neutralization sensitivities of the corresponding NL4-3 chimera containing the wild-type Env were evaluated for statistical significance by a Wilcoxon signed rank test, and P values are shown at the top of each box.