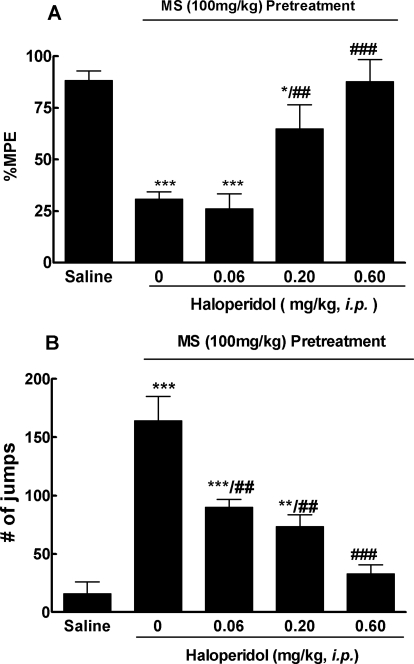
Fig. 3.
Reversal of acute opioid tolerance (A) and dependence (B) by haloperidol. Separate groups of six mice received morphine (100 mg/kg s.c.) or an equal volume of saline. Four hours later, haloperidol (0.06, 0.20, and 0.60 mg/kg i.p.) or saline was given to these mice. Thirty minutes later, all groups received a test dose of morphine (10 mg/kg s.c.) for the antinociception test. A, the established morphine-antinociceptive tolerance was reversed by haloperidol in a dose-dependent manner. B, development of morphine dependence, as revealed by 10 mg/kg i.p. naloxone-precipitated withdraw jumping, which was also reversed by haloperidol in a dose-dependent way. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 compared with the saline group; ##, p < 0.01; ###, p < 0.001 compared with the morphine (MS) alone group.