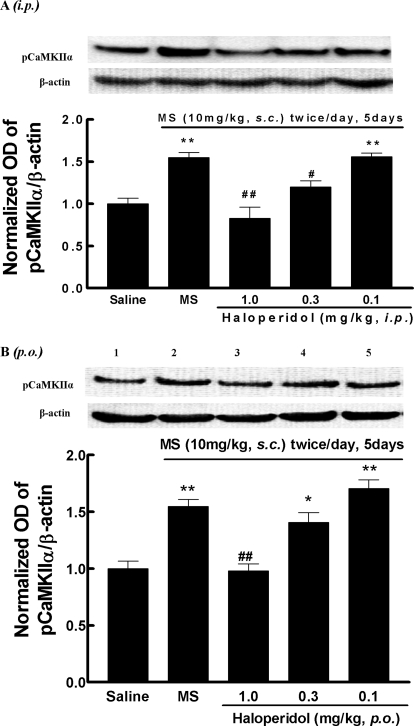
Fig. 6.
Effect of haloperidol on brain CaMKIIα activity in opioid-tolerant and -dependent mice (chronic model). Separate groups of three mice received morphine (10 mg/kg s.c.) or an equal volume of saline twice per day for 5 days. Thirty minutes before the last injection of morphine on day 5, mice were treated with haloperidol (A) (approximately 0.1–1.0 mg/kg i.p.), haloperidol (approximately 0.1–1.0 mg/kg p.o.) (B), or saline. Brain samples were taken 30 min after the last injection of morphine or saline. The activated CaMKIIα and total CaMKIIα were determined by the Western blotting method using antibodies specific for Thr286-pCaMKIIα and CaMKIIα, respectively. Histogram data, expressed as mean ± S.E.M., were constructed from the representative figure shown and three other experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 compared with the saline group; #, p < 0.05; ##, p < 0.01 compared with the morphine (MS) alone group.