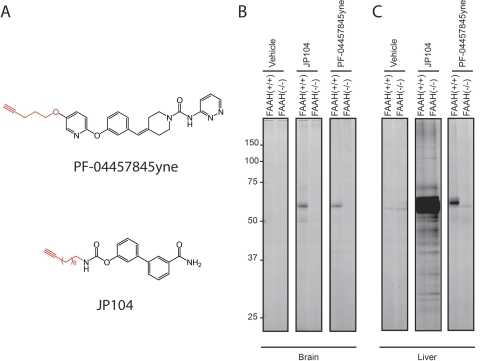
Fig. 5.
Assessment of in vivo protein targets of alkyne analogs of PF-04457845 and URB597 by CC-ABPP. A, structures of PF-04457845yne and JP104, alkyne analogs of PF-04457845 (top) and URB597 (bottom). B and C, gel profiles of CC-ABPP studies. Brain (B) or liver (C) mice proteomes were isolated after treatment with PF-04457845yne and JP104 for 2 h at 10 mg/kg i.p., reacted with a rhodamine-azide tag under CC conditions, and analyzed in-gel fluorescent scanning (shown in grayscale). PF-04457845yne selectively labels FAAH in both brain and liver tissues as shown [∼60-kDa band is absent in FAAH(−/−) mice], which is in contrast to JP104, which labels several additional proteins in liver [protein bands present in both FAAH(+/+) and FAAH(−/−) mice]. Note that the 55-kDa protein band observed in liver proteome from PF-04457845yne-treated FAAH(−/−) mice was also detected in liver proteomes from vehicle-treated FAAH(+/+) and FAAH(−/−) mice and therefore most likely represents a background protein that cross-reacts with the azide-rhodamine tag.